Nuts and bolts go hand in hand and without them producing a piece of strong equipment is almost impossible. They are specifically designed to strengthen any electrical equipment, automobiles, or spare parts they are holding together. Nuts have threaded holes and they are matched with bolts that are made to fit specific nuts. Bolts have a shank and a head. The cylindrical part is called a shank, which is threaded at the tail end. While all this sounds simple, you’ll be surprised after knowing how many different types of nuts and bolts exist. Rest assured we will also show types of nuts and bolts with pictures to clear out any confusion.
Let’s jump in!
Types of Nuts and Bolts
1. Types of Bolts (Generic)
- Square-headed bolt
- Hexagonal-headed bolt
- Cup-headed or round-headed bolt
- Countersunk-headed bolt
- Cylindrical or cheese-headed bolt
- T-headed bolt
2. Special Purpose Bolts
- Carriage bolt
- Stove bolt
- Expansion bolt
- Eye-bolt
- Stud
- Hook Bolt
- Foundation bolt
3. Types of Nut
- Square Nut
- Hexagonal Nut
- Cap Nut
- Cylindrical Nut
- Wingnut Nut
- Ring Nut
- Dome Nut
1. Types of Bolt (Generic)
1.1 Square-Headed Bolt

This type of bolt is most commonly used when its head has to be lodged in a recess. It prevents the bold from turning whenever the nut is screwed off or on. And for this reason, it is square. It is given a neck of square cross-section when it is used with a head projection outside. This also helps the bolt from rotating. The square-headed bolt is mainly used in a shaft’s bearings.
1.2 Hexagonal-headed bolt

The hexagonal-headed bolt is the most common type of bolt and is usually used in fasting or tightening. At the upper end, the hexagonal head is chamfered. Another spanner is used to stop the bolt from rotating when the nut is screwed on or off.
1.3 Cup-Headed or Round-Headed Bolt

The cup-headed bolt also known as the round-headed bolt is used where a better appearance is a priority. This bolt comes with a sung forged just below the head, which stops the bolt from rotating. This bolt is ideally used while manufacturing locomotives and tanks.
1.4 Countersunk-Headed Bolt
This bolt is most commonly used when the bolt must not be visible on the connection piece’s surface. It may be given with a neck or a snack to stop the bolt from rotating.

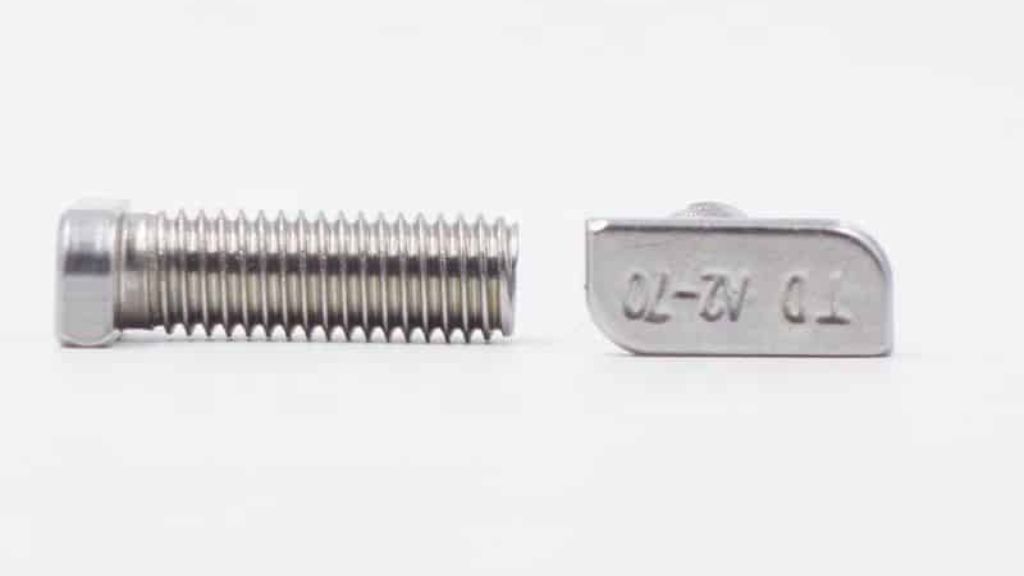
1.5 Cylindrical or Cheese-Headed Bolt

The cylindrical or cheese-headed bolt is used where the bolt-head arranging space is limited and unacceptable projecting corners. Just under the head, into the shank, a pin is inserted to prevent the bolt from rotating. The pin’s projecting part fits perfectly into the groove in the adjacent piece. The cylindrical bolt is used in eccentrics, connectors, and more.
1.6 T-Headed Bolt

The T-headed bolt is ideally used for fasting vices, clamps, and the machine tool’s tables. These tables have in-built T-slots to place the T-heads. To prevent the rotation of a T-bolt, the neck is built square in section.
Now that we have covered different types of bolts, let’s move on to special-purpose bolts.
2. Special Purpose Bolts:
Here we have mentioned a few special-purpose bolts:
2.1 Carriage Bolt
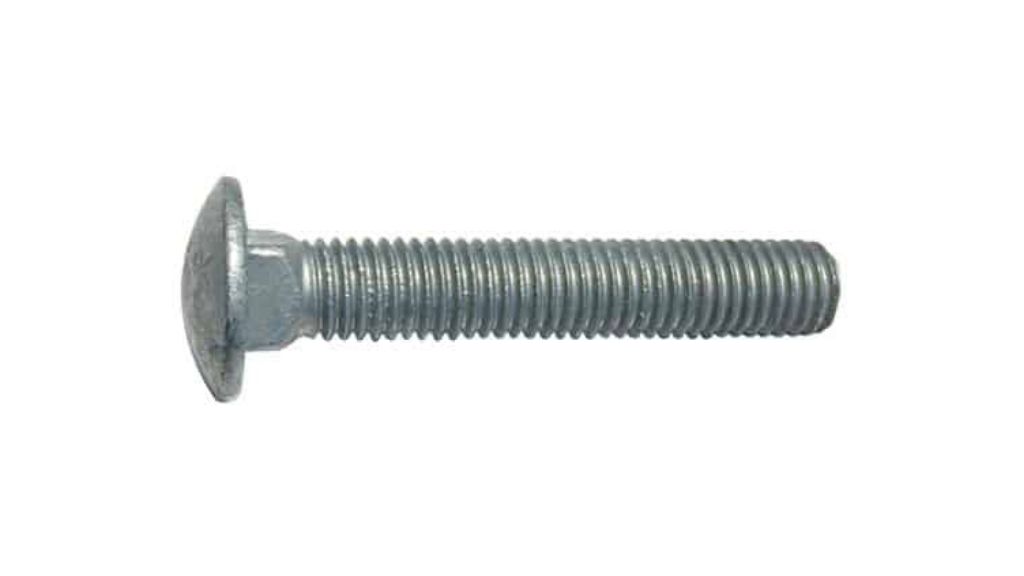

The Carriage bolt is generally used to tighten metal or wooden parts together. Under the head, a square portion is situated which helps in stopping the rotation when tightening the nut.
2.2 Stove Bolt
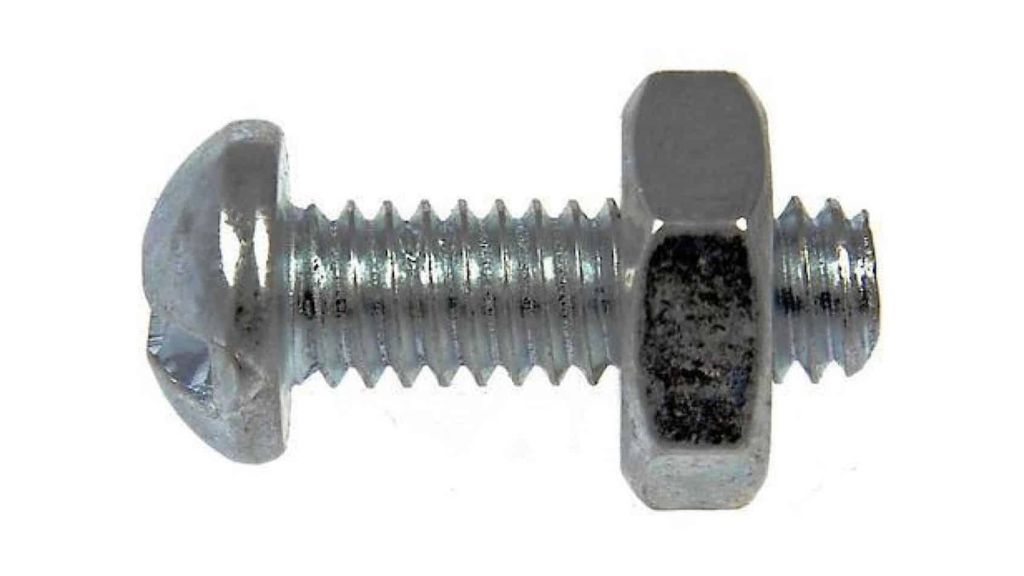

It has a flat and round head and it is used to fit a countersunk hole with a slot on its head. A screwdriver is needed to fasten the bolt into the nut. It can be used in assemblies where precision is not the requirement. The head of the bolt must be flush with the work surface.
2.3 Expansion Bolt
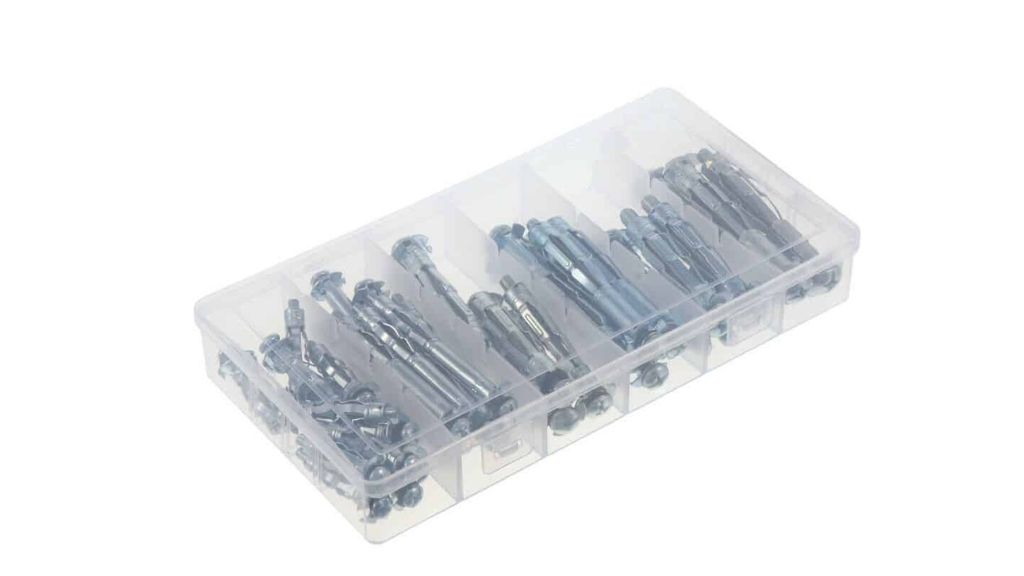

The expansion bolt is applied while joining parts of stones, bricks, or concrete walls. This bolt’s internally threaded split sleeve is put in the hole made in the wall and then further a screw is used to expand it.
2.4 Foundation Bolt
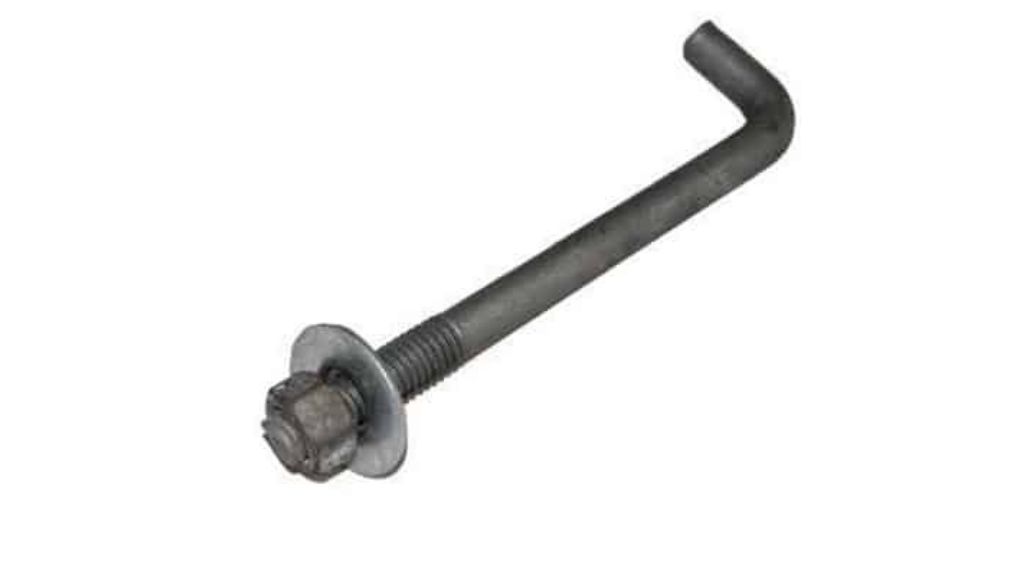

The foundation bolt also known as the rag bolt is applied to the stone concrete foundation. This type of bolt’s bottom head is usually wider than the top. This bolt’s tapered head is unevenly cut and then molten lead or sulfur is poured into the taper hole to fill the gap between the stone and the lead. If more strength is needed in the construction, four parallel keys or bars are used.
2.5 Eye-Bolt
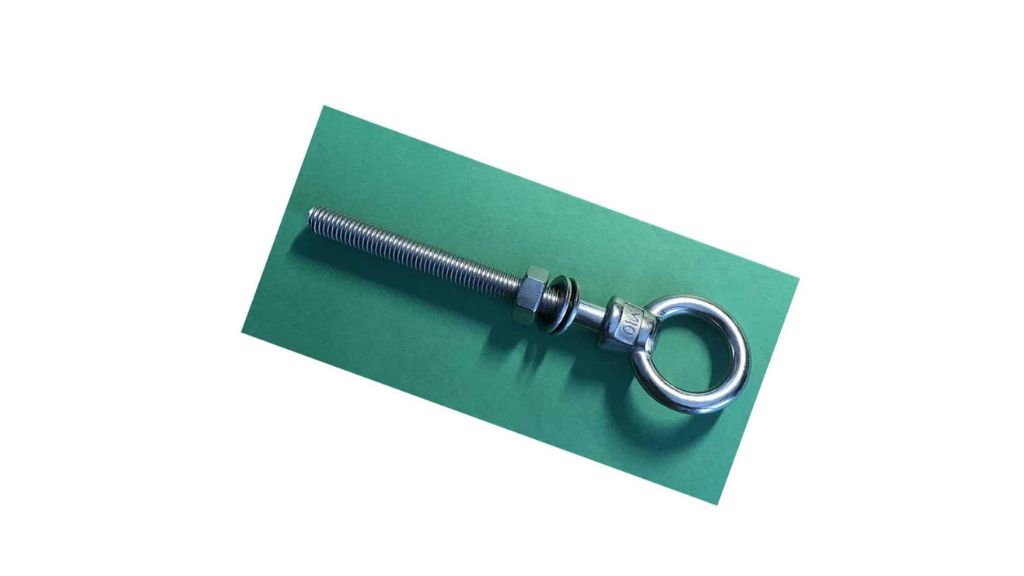

This bolt is usually used in lifting. On top of the machine, this bolt is turned inside a threaded hole or screwed on the head of the machine. One or more eye-bolts are fixed on medium/lightweight machinery and electric motors to make them lift ready and carried by a crane.
2.6 Stud
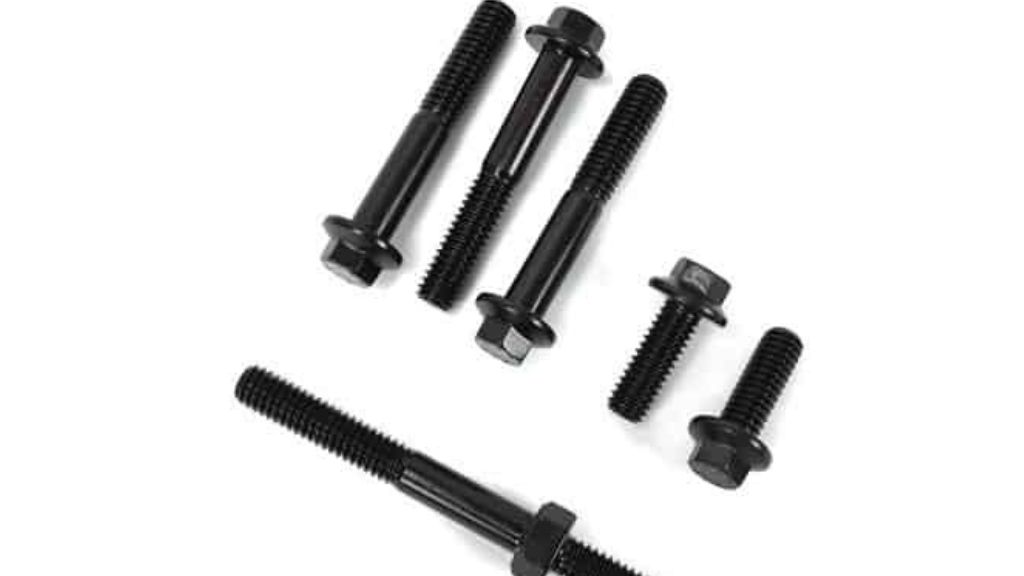

In a stud, a cylindrical steel piece is screwed at both ends. There is no head present in a bolt and the threaded nut-end is slightly thicker than the nuts that are to be used. The metal end is threaded for an equal length of the diameter of the stud. It is the most commonly used to cover engine cylinders.
2.7 Hook Bolt
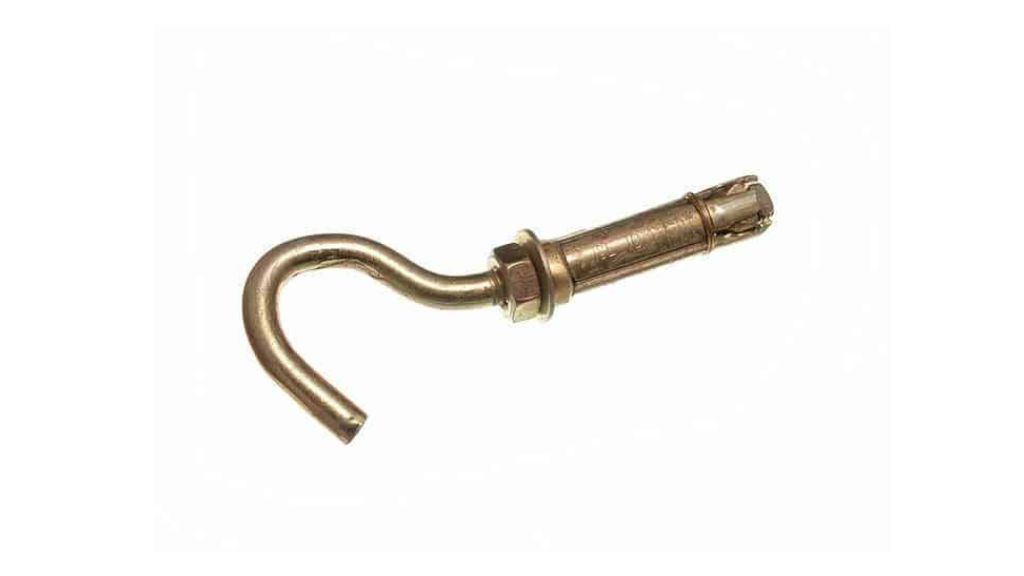

This bolt is generally applied while semi-permanent tightening the concrete. The hook bolt is also ideal for its application where there is no space for a bolt hole or a bolt hole can weaken a piece. Therefore, the hook bolt is perfect for joining shaft hangers to flanges of girders and joists.
After finishing the list of types of bolts, let’s jump into the types of nuts.
3. Types of Nuts
A nut is essential to efficiently tighten a bolt or a stud. Here are the types of nuts:
3.1 Square Nut
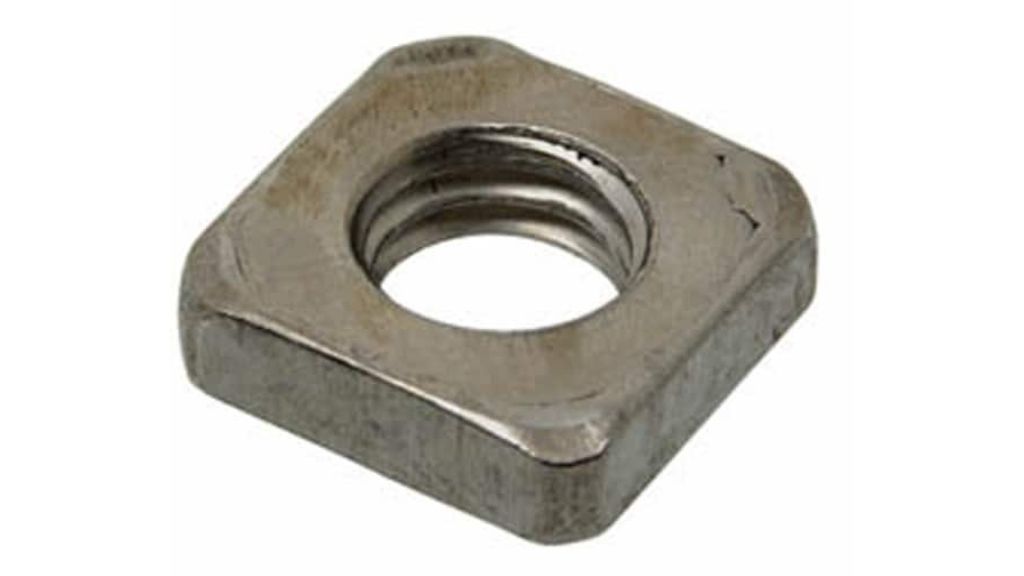

It is typically used together with a square-headed bolt. Due to its square shape, the spanner has a better grip as compared to a hexagonal nut.
3.2 Hexagonal Nut
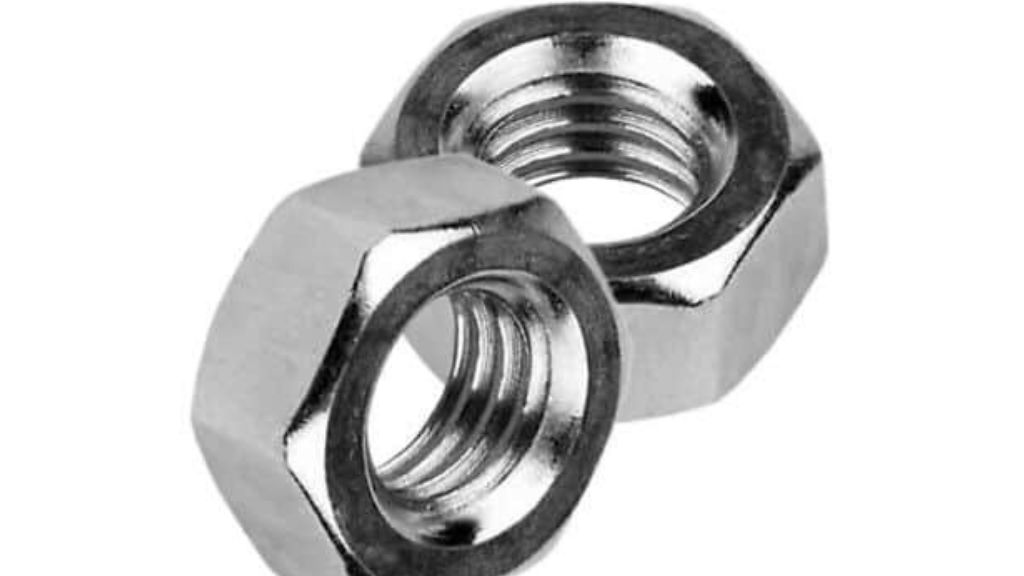

One of the most common nuts that are utilised for tightening and fastening is a Hexagonal Nut. It is best-suited with a hexagonal-headed nut.
3.3 Cap Nut
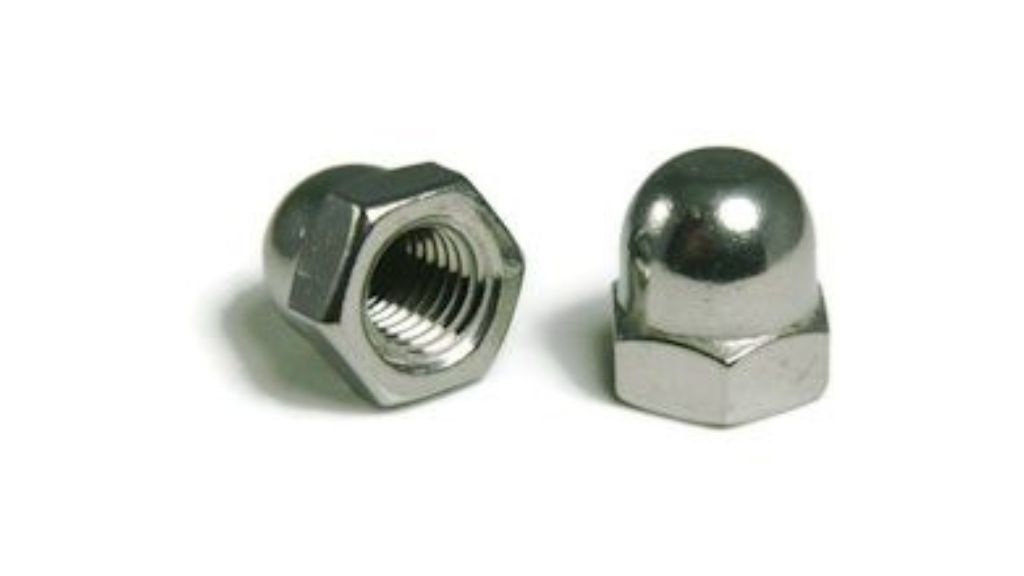

The cap nut is also a type of hexagonal nut but with a cylindrical cap on the top to prevent corrosion. Typically used in smoke-boxes locomotives, it stops leakage from the threads.
3.4 Cylindrical Nut

The cylindrical nut also known as the capstan nut is cylindrical. On its curved surface, holes are drilled to help it turn with a Tommy bar.
3.5 Wingnut Nut

A wingnut is also known as the thumb nut got its name from its ease of use with a thumb and a finger. It is ideal for parts where it is required to adjust frequently.
3.6 Ring Nut

As the name suggests, the nut is in the form of a ring and a special c-spanner is used for it. This nut is typically used in spare parts as a nut to lock the other nuts.
3.7 Dome Nut
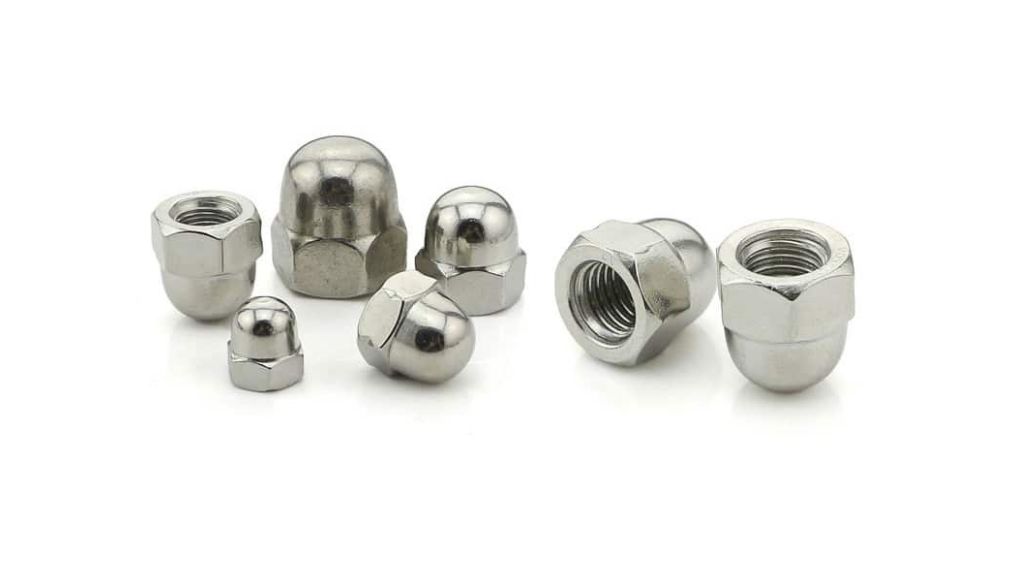

Dome nuts have a dome shape on one side of the nut. These nuts are most commonly used to safeguard objects closer to screws from structural injuries.
Types of Nuts and Bolts in Summary
Quite evidently, nuts and bolts are one of the most significant parts of a building or a mechanical product. However, it is also important to select the right nuts and bolts before starting a project because if not properly chosen, your project may fall apart.






