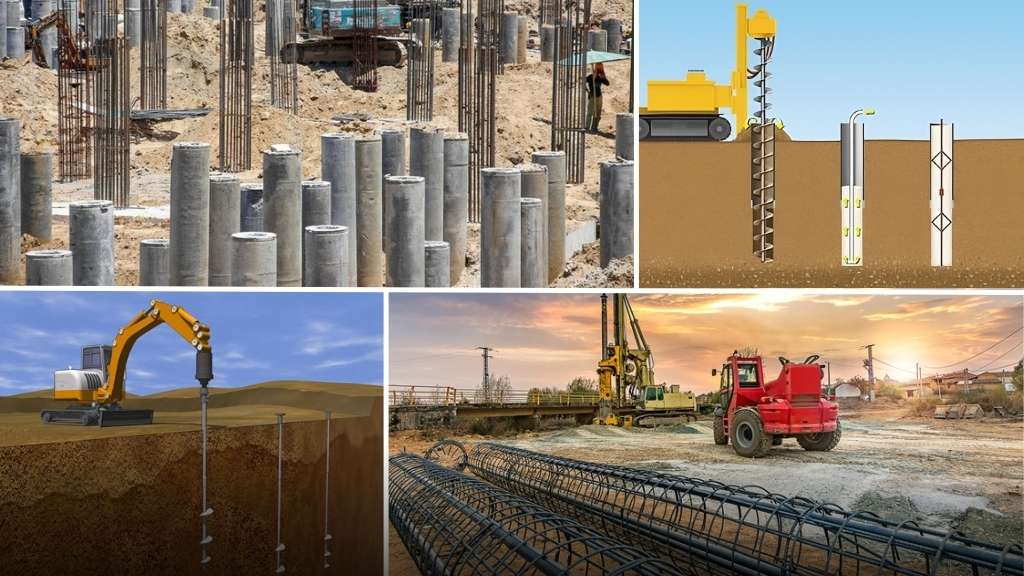

Construction on unstable or weak soil often poses significant challenges, leading to risks of structural failure. Without a strong foundation, buildings may face issues like settlement or instability over time. This is where pile foundations come into play, providing the necessary support by transferring loads to deeper, stronger soil layers.
But with various types of pile foundations available, how do you determine the right one for your project? In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of pile foundations in construction and their specific applications for safe and durable structures.
Whether you are a student of civil engineering, a construction professional, or a curious reader, this article will provide you with an overview of the types of pile foundations and their uses in construction.
What is Piles Foundation? What are its Advantages?
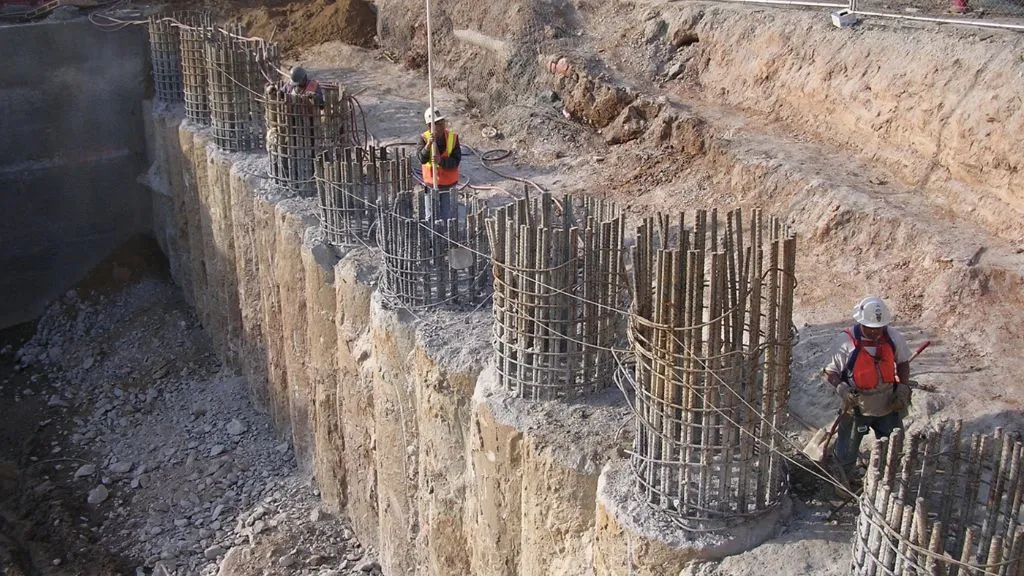

A pile foundation is a deep foundation used to transfer a structure’s load to a deeper and stronger layer of soil or rock. Pile foundations are typically used when the surface soil is not strong enough to support the weight of the structure, or when the structure has a heavy load that requires a deeper foundation.
Pile foundations consist of long, slender, and cylindrical elements that are driven, drilled, or jacked into the ground to provide support for the structure. The piles are typically made of concrete, steel, or timber, and they can be driven or drilled to a depth of 20 meters or more.
Pile foundations are commonly used in construction projects such as bridges, high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and transportation infrastructure. A geotechnical engineer can help determine the most appropriate type of pile foundation for a particular project, based on the specific site conditions and load requirements.
How Many Different Types of Piles Foundations Used in Construction?
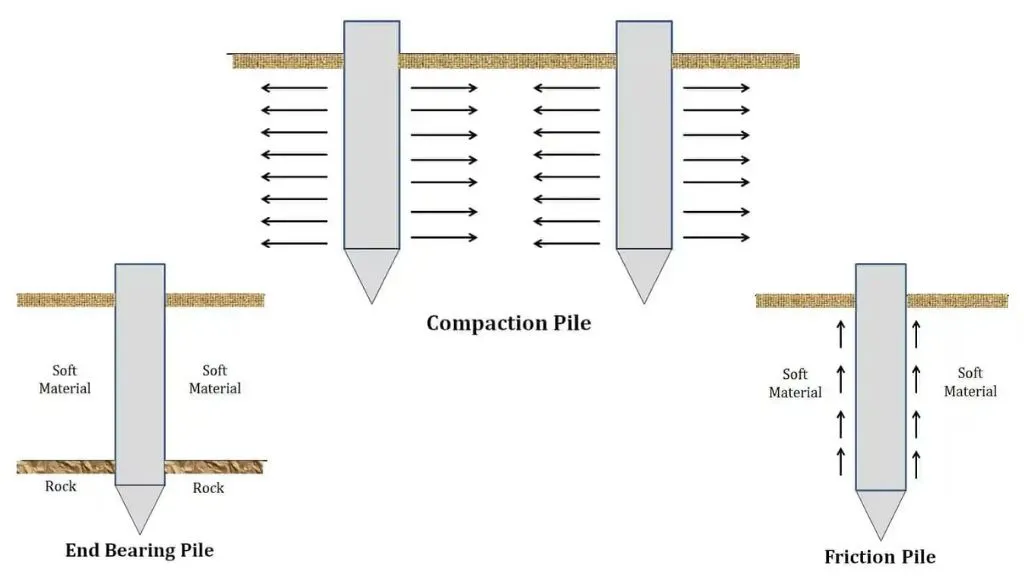
1. End Bearing Piles
These piles are designed to transfer the load of the structure to a strong layer of rock or other material at the bottom of the pile. The pile is typically made of reinforced concrete or steel, and it is driven deep into the ground until it reaches the load-bearing layer. End bearing piles are commonly used for structures with heavy loads, such as bridges and high-rise buildings.
2. Friction Piles
These piles are designed to transfer the load of the structure to the soil along the length of the pile. The pile is typically made of reinforced concrete or steel, and it is driven deep into the ground until it reaches a soil layer that can support the load. Friction piles rely on the friction between the pile and the soil to transfer the load. They are commonly used for structures with moderate to heavy loads.
3. Compaction Piles
These piles are formed by compacting the soil in place using a hydraulic ram or other similar methods. The compacted soil forms a strong column that can support the load of the structure. A casing is typically used to contain the soil during the compaction process. Once the pile is formed, the casing is removed. Compaction piles are typically used for structures with light to moderate loads, and they are particularly useful for soft or loose soil.
4. Bored Piles
These piles are formed by drilling a hole into the ground and then filling it with concrete or other material. The hole is typically reinforced with a steel casing, and it is drilled to the required depth. Once the hole is drilled, it is filled with concrete, and a steel reinforcement cage is inserted into the concrete. Bored piles are commonly used for structures with heavy loads, and they are particularly useful in areas where noise and vibration need to be minimized.
5. Driven Piles
These piles are formed by driving a precast concrete, steel, or timber pile into the ground using a pile driver. The pile is typically driven to a depth of 20 to 30 times its diameter. Driven piles are commonly used for structures with moderate to heavy loads, and they are particularly useful in areas with hard soil or rock.
In addition to these five types of pile foundations, there are also several variations of these types. For example, combination piles can be formed by combining two or more of these types of piles in construction to provide the required load-bearing capacity. The choice of pile foundation type depends on various factors, such as the soil conditions, the type of structure, the load to be supported, and the budget. A geotechnical engineer can help determine the most appropriate type of piles foundation for a particular project.
When to Use Piles Foundation?
1. Soft or Loose Soil
When the soil at the ground surface is soft or loose, it may not be able to support the weight of the structure. This can occur in areas with thick layers of clay or loose sediment. Pile foundations are used to transfer the load of the structure to a deeper layer of soil or rock that can provide sufficient support. The piles can be driven through the soft soil until they reach a layer of soil or rock that can provide the necessary support.
2. High Water Table
When the water table is high, the soil may become saturated and lose its strength. This can occur in coastal areas or in areas with high rainfall. Pile foundations can be used to transfer the load of the structure to a deeper and drier layer of soil or rock. The piles are driven through the saturated soil until they reach a layer of soil or rock that is not affected by the water table.
3. Heavy Loads
When the structure has a heavy load, such as in the case of tall buildings, bridges, or industrial facilities, pile foundations can be used to transfer the load to a deeper and stronger layer of soil or rock. The piles are designed to resist the weight of the structure and the loads that will be placed on it.
4. Sloping or Uneven Ground
When the g round surface is sloping or uneven, it may be difficult to construct a traditional shallow foundation. Pile foundations can be used to provide support for the structure by driving piles into the ground at an angle or by using piles of different lengths to compensate for the slope.
5. Expansive Soil
When the soil is prone to swelling and shrinking due to changes in moisture content, pile foundations can be used to transfer the load of the structure to a deeper and more stable layer of soil or rock. The piles can be designed to resist the movements of the soil and provide a stable foundation for the structure.
Final Thoughts
Pile foundations are essential to modern construction projects, providing necessary support for structures with heavy loads or unstable soil conditions. The different types of piles in the foundation, including driven, bored, and cast-in-place, offer engineers and construction professionals a range of options to ensure a stable and secure foundation for their projects.
Choosing the appropriate pile foundation type requires a thorough analysis of site conditions, load requirements, and project specifications. With the right selection and installation of pile foundations, builders can achieve long-lasting and structurally sound buildings and infrastructure. By understanding the types of pile foundations, construction professionals can make informed decisions that ensure the safety and durability of the structures they build.






