
Plumbing and sanitary systems are crucial for the functionality and hygiene of any building. From water supply to drainage systems, the right plumbing and sanitary items ensure smooth operations and prevent costly issues in the future.
Understanding the essential items required for construction can help builders and homeowners make informed decisions during the planning and execution phases. In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive list of plumbing and sanitary items commonly used in construction, highlighting their roles and importance in creating efficient, long-lasting systems.
Plumbing and Sanitary Items List Used For Construction & Every Home
1. Pipes:
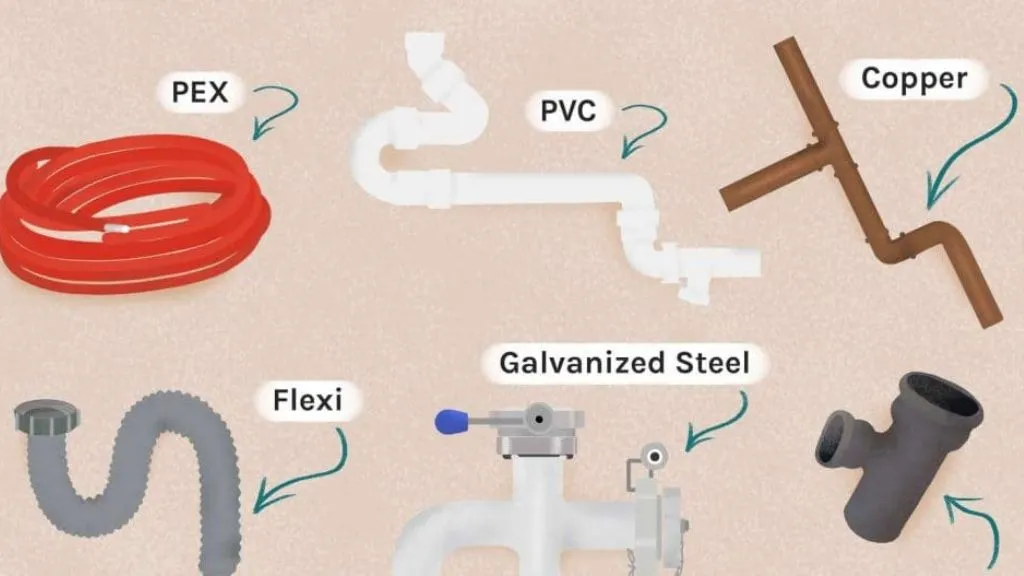
Pipes are tubular structures used to convey fluids or gases from one location to another. They come in various materials, sizes, and configurations, depending on their intended use. The choice of pipe material depends on factors such as cost, durability, pressure requirements, and compatibility with the conveyed fluid. Here are some commonly used types of pipes in construction:
- Copper pipes: Copper pipes are widely used for water supply lines due to their excellent corrosion resistance and durability. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for both residential and commercial applications. Copper pipes are available in two main types: rigid copper pipes (Type M, L, and K) and flexible copper pipes (also known as copper tubing).
- PVC pipes: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to install. They are commonly used for drainage, waste, and vent (DWV) systems. PVC pipes are available in different sizes and classes (Schedule 40 and Schedule 80) to accommodate various pressure requirements.
- PEX pipes: Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes have gained popularity due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to temperature variations. PEX pipes are commonly used for water supply lines, especially in residential applications. They are available in different colors (red for hot water, blue for cold water) and can be easily bent and maneuvered around obstacles.
- Galvanized steel pipes: Galvanized steel pipes are coated with a layer of zinc to protect against corrosion. They are commonly used for water supply lines in older buildings but have become less popular due to the emergence of more corrosion-resistant materials like copper and PEX.
- HDPE pipes: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are known for their durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility. They are commonly used for underground water supply and irrigation systems. HDPE pipes are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can withstand high pressures.
2. Pipe Fittings
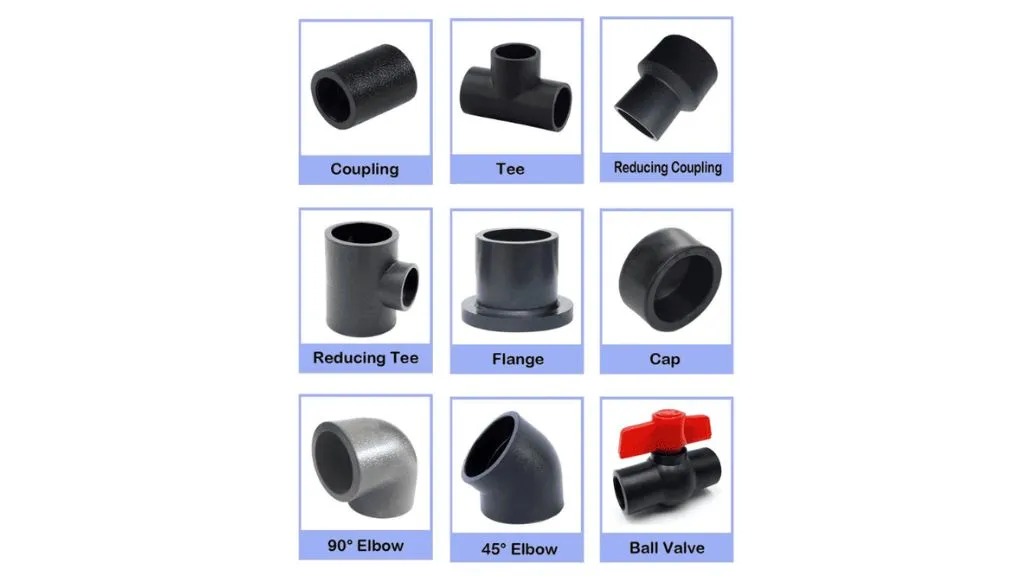

Pipe Fittings are used to connect, join, or change the direction of pipes, ensuring a leak-proof and functional plumbing system. They come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, and each serves a specific purpose. Here are some commonly used fittings in construction:
- Elbows: Elbows are fittings that allow a change in the direction of a pipe. The most common types are 90-degree elbows and 45-degree elbows. They are essential for navigating around obstacles and creating bends in the plumbing system.
- Tees: Tees have a T-shaped design and are used to create a branch connection in a pipe system. They allow the flow of water or gases to split into two or more directions. Tees are commonly used when adding fixtures or appliances to the plumbing system.
- Couplings: Couplings are fittings used to join two pipes of the same diameter in a straight line. They are typically used for repairs, extensions, or when a continuous pipe connection is required.
- Adapters: Adapters, also known as reducers, are fittings used to connect pipes of different sizes. They allow for a smooth transition between different pipe diameters, ensuring a proper fit and flow of fluids.
- Valves: Valves are essential fittings used to control the flow of water or gases within a plumbing system. They can start, stop, or regulate the flow and are available in various types such as gate valves, ball valves, check valves, and globe valves. Valves provide control and isolation points within the plumbing system, allowing for maintenance, repairs, and water conservation.
- Unions: Unions are fittings that provide a detachable connection between two pipes. They consist of three components: a nut, a male end, and a female end. Unions facilitate easy disassembly and reassembly of pipes, making them useful for maintenance and repairs.
- Flanges: Flanges are flat, circular fittings used to connect pipes or equipment with bolts and gaskets. They provide a secure and leak-resistant connection, commonly used in larger piping systems or equipment connections.
- Reducers: Reducers are fittings used to transition from a larger pipe size to a smaller one or vice versa. They help maintain a consistent flow rate and pressure when connecting pipes of different diameters.
3. Water Pumps
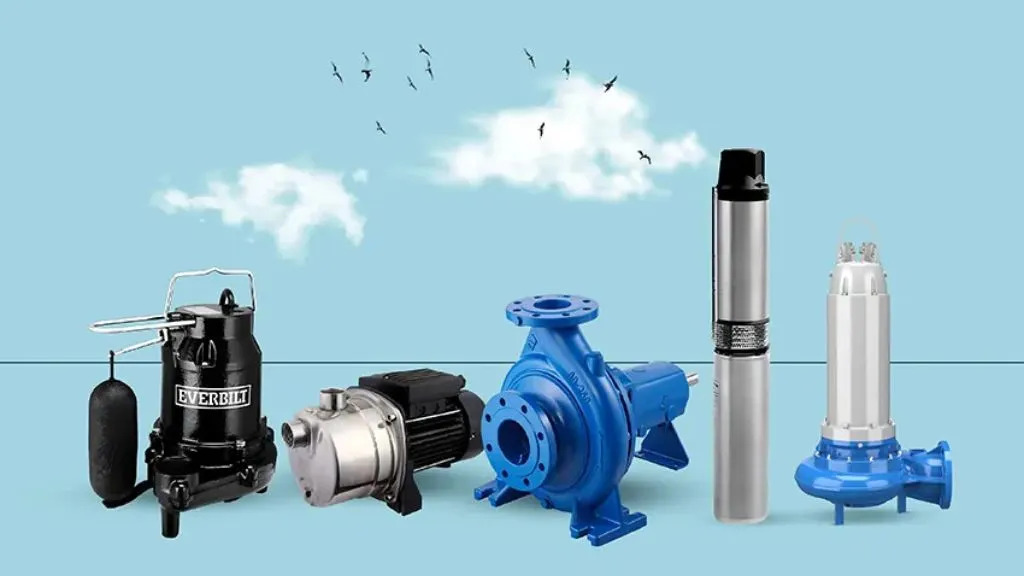

Pumps are mechanical devices used to transfer fluids or gasses from one location to another within a plumbing system. They are essential for maintaining water pressure, circulating water in heating systems, removing wastewater, and ensuring the proper functioning of the plumbing system. Here are some commonly used types of pumps in construction:
- Water pumps: Water pumps are widely used for boosting water pressure, supplying water to fixtures, and circulating water in heating and cooling systems. They come in various types, including centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps, and jet pumps. Water pumps are selected based on factors such as flow rate, pressure requirements, and the type of application (domestic, commercial, or industrial).
- Sump pumps: Sump pumps are typically installed in basements or crawl spaces to remove excess water and prevent flooding. They automatically activate when the water level reaches a certain height, pumping the water out of the designated area and directing it away from the building. Sump pumps are critical for protecting basements from water damage and maintaining a dry environment.
- Sewage pumps: Sewage pumps are designed to transport wastewater containing solids from a building to the municipal sewer system or a septic tank. They are specifically designed to handle the corrosive and abrasive nature of sewage. Sewage pumps are available in various configurations, including submersible pumps and grinder pumps, depending on the application and the type of waste to be handled.
- Booster pumps: Booster pumps are used to increase water pressure in plumbing systems. They are commonly employed in multi-story buildings or areas with low water pressure. Booster pumps ensure adequate water pressure for fixtures and appliances, providing a comfortable and efficient water supply.
4. Sanitary Fixtures
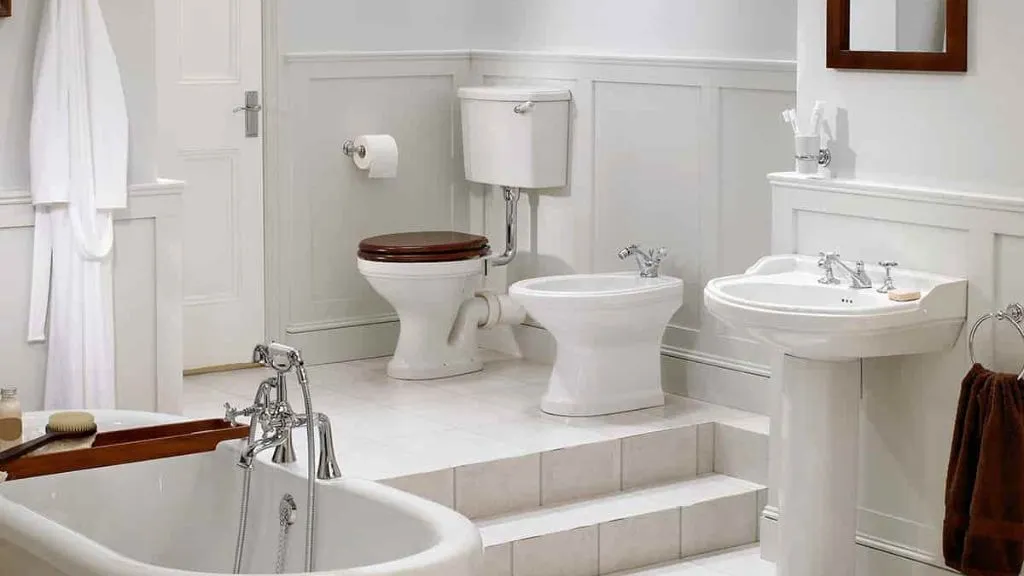

Fixtures are plumbing devices that provide access to water and drainage in buildings. They are installed in specific locations for various purposes, such as bathing, washing, and waste disposal. Fixtures come in a wide range of designs, styles, and functionalities. Here are some commonly used bathroom fixtures in construction:
- Faucets: Faucets, also known as taps, are used to control the flow of water from the plumbing system. They are installed at sinks, basins, showers, bathtubs, and other water outlets. Faucets come in different styles, such as single-handle faucets, double-handle faucets, and touchless faucets. They are available in various materials, including chrome, brass, stainless steel, and nickel, offering both functionality and aesthetics.
- Toilets: Toilets are essential sanitary fixtures used for human waste disposal. They consist of a bowl, a water tank, and a flushing mechanism. Toilets come in different types, including one-piece toilets, two-piece toilets, wall-hung toilets, and water-saving toilets. Modern toilets often feature water-efficient flushing systems to minimize water consumption.
- Sinks: Kitchen Sinks are fixtures used for handwashing, dishwashing, and other cleaning purposes. They are installed in kitchens, bathrooms, and utility areas. Sinks come in various styles, such as pedestal sinks, under-mount sinks, top-mount sinks, and vessel sinks. They can be made from materials like stainless steel, ceramic, or composite materials, offering durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Showers: Showers are fixtures designed to deliver a spray of water for bathing. They can be standalone units or part of a bathtub enclosure. Showers come in different configurations, including showerheads, handheld showers, rain showers, and body spray systems. They often feature adjustable water pressure and temperature controls for a personalized bathing experience.
- Bathtubs: Bathtubs are fixtures used for bathing and relaxation. They come in various shapes and sizes, such as alcove bathtubs, freestanding bathtubs, and corner bathtubs. Bathtubs can be made from materials like acrylic, fiberglass, or cast iron, providing options for aesthetics and durability.
- Urinals: Urinals are fixtures commonly found in public restrooms or commercial settings. They are designed for male users and provide a more water-efficient alternative to traditional toilets. Urinals come in various styles, including wall-mounted urinals and waterless urinals, promoting water conservation and hygiene.
4. Water Heaters
- Tank Water Heaters
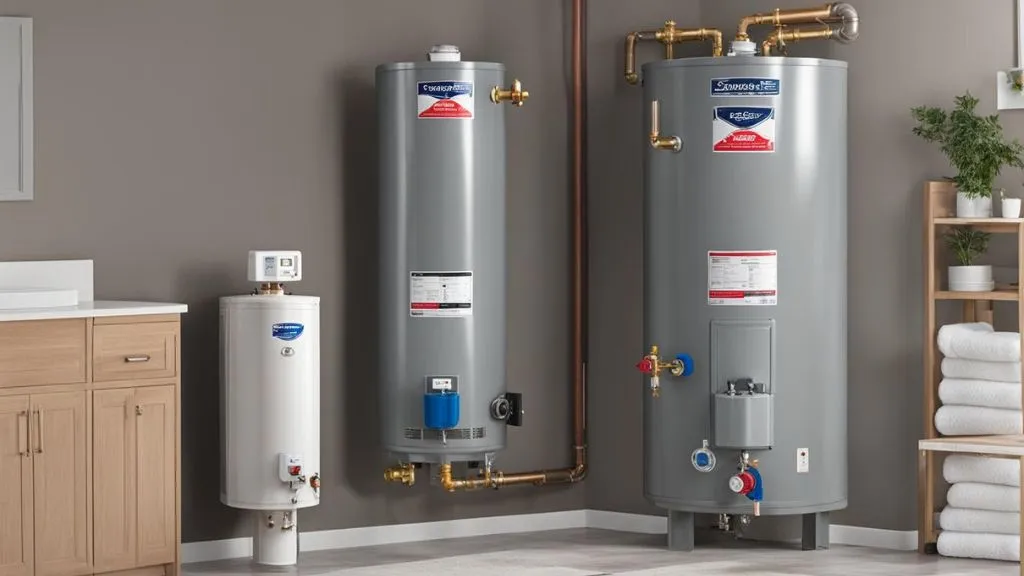

Tank water heaters, also known as storage water heaters, are the most common type of water heaters. They consist of an insulated tank that stores and heats a specific volume of water. Here are the key components and features of tank water heaters:
- Tank: The tank is a cylindrical or rectangular container made of steel, stainless steel, or glass-lined material. It is insulated to minimize heat loss and maintain the temperature of stored water.
- Heating element: The heating element, typically an electric resistance element or a gas burner, is located at the bottom of the tank. It heats the water to the desired temperature.
- Thermostat: The thermostat controls the temperature of the water by monitoring and adjusting the heating element’s operation. It ensures that the water remains at a consistent temperature for immediate use.
- Temperature and pressure relief valve (TPR Valve): The TPR valve is a safety device installed on the tank to release excess pressure and prevent the tank from exploding in case of overheating or high pressure.
- Anode rod: Anode rods are sacrificial rods made of aluminum or magnesium that are inserted into the tank to prevent corrosion. They attract corrosive elements, protecting the tank from rust and extending its lifespan.
- Dip tube: The dip tube is a pipe that allows cold water to enter the tank at the bottom, ensuring that it is heated from the bottom up.
- Tankless Water Heaters
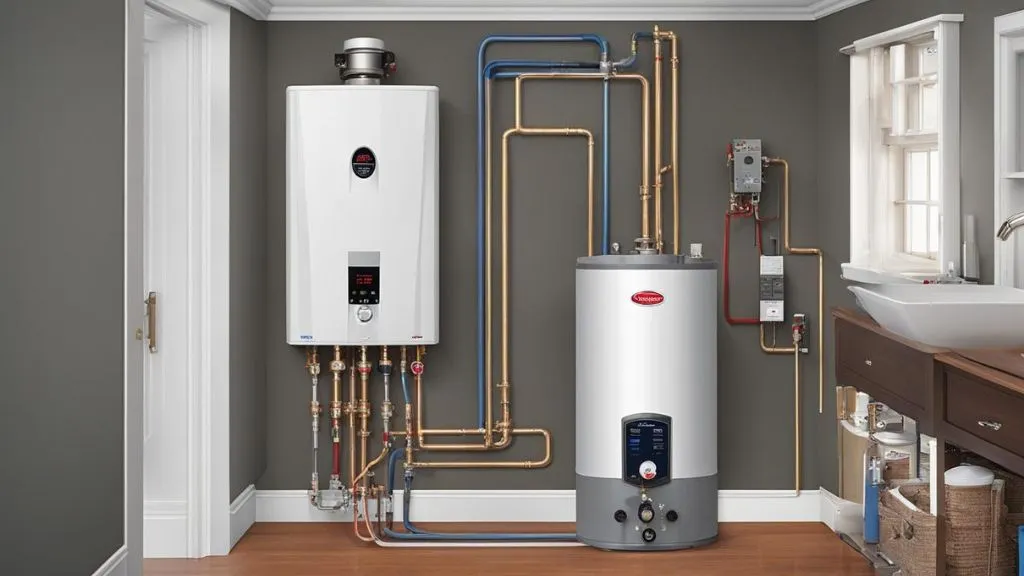

Tankless water heaters, also known as on-demand water heaters or instantaneous water heaters, provide hot water only when needed, without the need for a storage tank. Here are the key components and features of tankless water heaters:
- Heat exchanger: Tankless water heaters use a heat exchanger, typically made of copper or stainless steel, to heat the water directly as it passes through the unit. The heat exchanger rapidly heats the water to the desired temperature.
- Burner or heating element: Tankless water heaters use either a gas burner (natural gas or propane) or an electric heating element to generate heat for the heat exchanger.
- Flow sensor: A flow sensor detects the flow of water and activates the heating element or burner when hot water is demanded. The heating element or burner remains active as long as there is a demand for hot water.
- Temperature control: Tankless water heaters have temperature controls that allow users to set the desired hot water temperature.
- Space efficiency: Tankless water heaters are compact and do not require a storage tank, making them ideal for smaller spaces and reducing standby heat loss.
- Heat Pump Water Heaters
Heat pump water heaters (HPWH) use electricity to transfer heat from the surrounding air or ground to heat the water. They work on the same principle as air conditioners but in reverse. Here are the key components and features of heat pump water heaters:
- Heat pump unit: The heat pump unit extracts heat from the air or ground using a refrigerant and compressor. The heat is transferred to the water in the storage tank.
- Storage tank: Heat pump water heaters have a storage tank similar to tank water heaters to store heated water.
- Controls: HPWHs have controls to regulate the heating process, temperature, and energy efficiency settings.
- Energy efficiency: Heat pump water heaters are known for their high energy efficiency. They can be up to three times more efficient than conventional electric water heaters, as they transfer heat rather than generate it.
- Solar Water Heaters
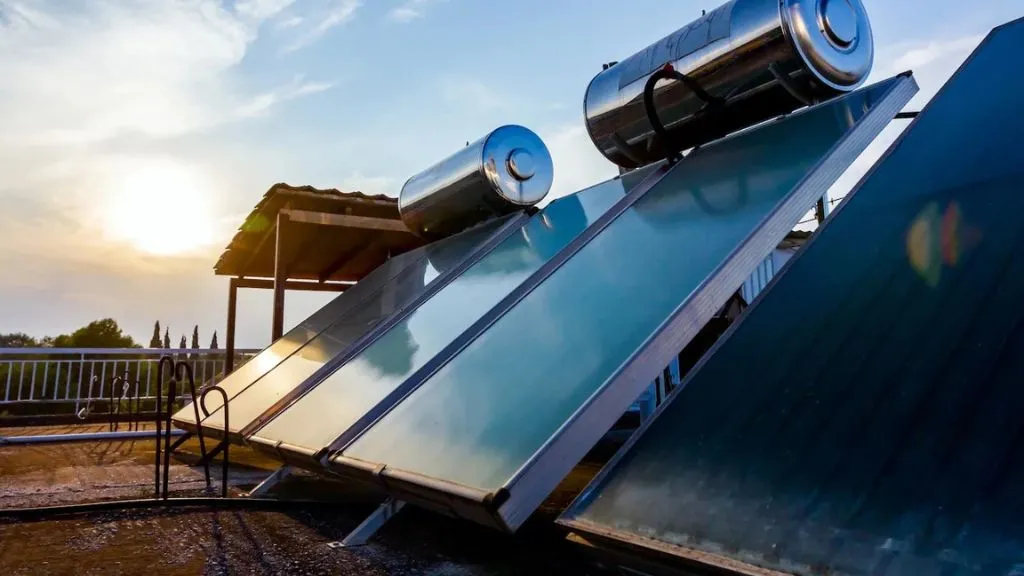

Solar water heaters utilize energy from the sun to heat water. They consist of solar collectors, storage tanks, and backup systems (such as electric or gas heaters). Here are the key components and features of solar water heaters:
- Solar collectors: Solar collectors, usually mounted on the roof or in an open area with maximum sunlight exposure, absorb solar radiation and convert it into heat. They can be flat-plate collectors or evacuated tube collectors.
- Heat transfer fluid: A heat transfer fluid, typically a mixture of water and antifreeze, circulates through the solar collectors, absorbs the heat, and transfers it to the water in the storage tank.
- Storage tank: Solar water heaters have a storage tank to store hot water. The storage tank can be a traditional tank or a specialized tank with additional insulation to minimize heat loss.
- Backup system: Solar water heaters often include a backup system, such as an electric or gas water heater, to provide hot water during periods of low sunlight or high demand.
- Controls: Solar water heaters have controls to regulate the flow of heat transfer fluid, monitor temperature, and manage the backup system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the plumbing and sanitary items list is an integral component of construction projects, facilitating the safe and efficient transport of water, gases, and waste materials. Pipes and fittings play a crucial role in connecting and directing the flow of fluids, while pumps ensure the proper movement and pressure of water within the plumbing system.
Fixtures provide access to water and drainage for various purposes, enhancing comfort and convenience.
Understanding the different types, materials, and functionalities of pipes, fittings, pumps, and fixtures is essential for designing and constructing reliable plumbing systems.
The choice of these components depends on factors such as the intended application, pressure requirements, durability, energy efficiency, and water conservation.
By selecting the appropriate plumbing and sanitary items, architects, engineers, contractors, and homeowners can ensure the functionality, safety, and longevity of the plumbing system.






