Property Geek
We provide the actual and accurate information with unbiased user driven reviews to our viewers, to help them see the best and find the best!
View posts
Windows are not just functional elements of a house; they are also vital contributors to its aesthetics, energy efficiency, and overall comfort. Among the various decisions homeowners face when selecting or replacing windows, one of the most critical is the choice of glass. With numerous types of glasses available, each offering distinct properties and benefits, understanding the differences is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your needs and preferences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore 11 different types of glasses and their applications, helping you elevate your home to new heights of style and functionality.
1. Float Glass
Pros
Optimal light transmission. Sleek aesthetic.
Cons
Lacks thermal insulation. Shatters into sharp pieces.
2. Annealed Glass
Pros
Versatile and affordable. Provides clear view.
Cons
Relatively low strength. Breaks into large, sharp pieces.
3. Heat Strengthened Glass
Pros
Increased strength. Safety and durability.
Cons
Not as strong as tempered glass. Breaks into large, sharp pieces.
4. Tempered Glass
Pros
High strength. Safety feature upon breakage. Enhanced security.
Cons
Difficult to cut or drill. Cannot be recut after tempering. More expensive.
5. Heat Soak Tempered Glass
Pros
Reinforced strength and durability. Eliminates defects. Exceptional safety.
Cons
Costlier than regular tempered glass. Limited availability.
6. Laminated Glass
Pros
Safety and security. Resistant to forced entry. Soundproofing and UV protection.
Cons
Can be heavier. More expensive than annealed glass.
7. Insulated Glass
Pros
Superior insulation. Energy efficient. Year-round comfort.
Cons
Higher initial cost. Seals may degrade over time.
8. Gas Filled Glass
Pros
Improved insulation. Energy efficiency. Suitable for extreme climates.
Cons
Higher initial cost. Seals may degrade over time.
9. Low-E Glass
Pros
Temperature regulation. UV protection. Energy efficiency.
Cons
Higher initial cost. Coating may require special care.
10. Tinted Glass
Pros
Heat and glare reduction. Privacy. Aesthetic enhancement.
Cons
Reduced natural light. Limited shade availability.
11. Obscured Glass
Pros
Privacy without sacrificing light. Adds character. Provides discretion.
Cons
Limited visibility. Limited design options.

Float glass serves as the foundation for most modern windows. These types of glasses boast a flat, even surface that allows for optimal light transmission and clarity. This type of glass is commonly used for standard window panes, providing a clear view of the surrounding environment while maintaining a sleek and contemporary aesthetic.
Among the different types of glasses, annealed glass is a variant of float glass that undergoes a slow cooling process, resulting in ordinary window glass before any additional treatments. Its versatility makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications, from residential windows to commercial storefronts. Annealed glass offers a balance of affordability and functionality, providing a clear view while offering a level of durability suitable for everyday use.
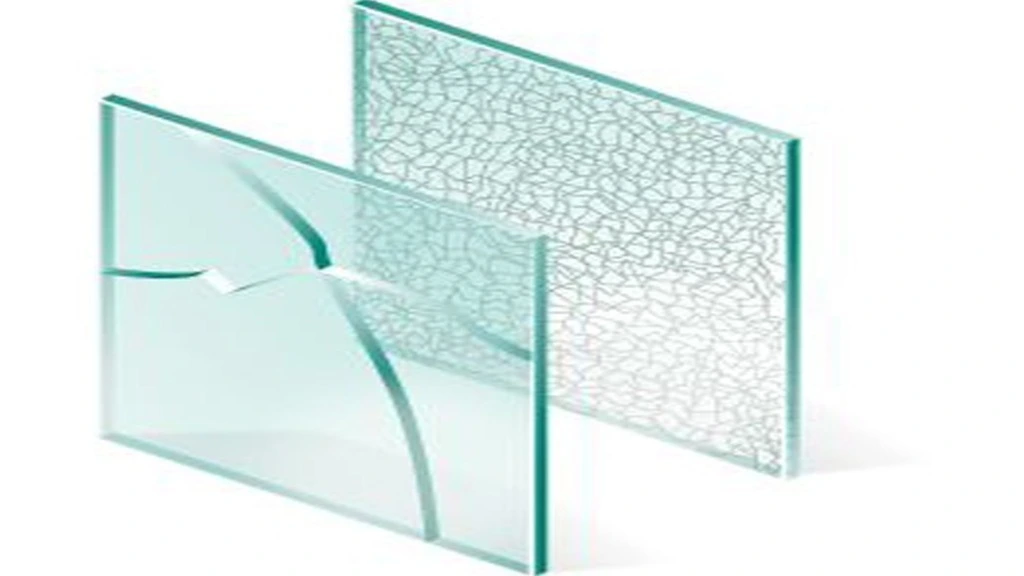

The heat-strengthened glass starts as annealed glass but undergoes additional processing to enhance its strength. Through rapid reheating and cooling, this glass becomes twice as strong as regular annealed glass, making it an ideal choice for areas where safety and durability are paramount. Heat-strengthened toughened glass design offers peace of mind while maintaining visual clarity and aesthetic appeal.
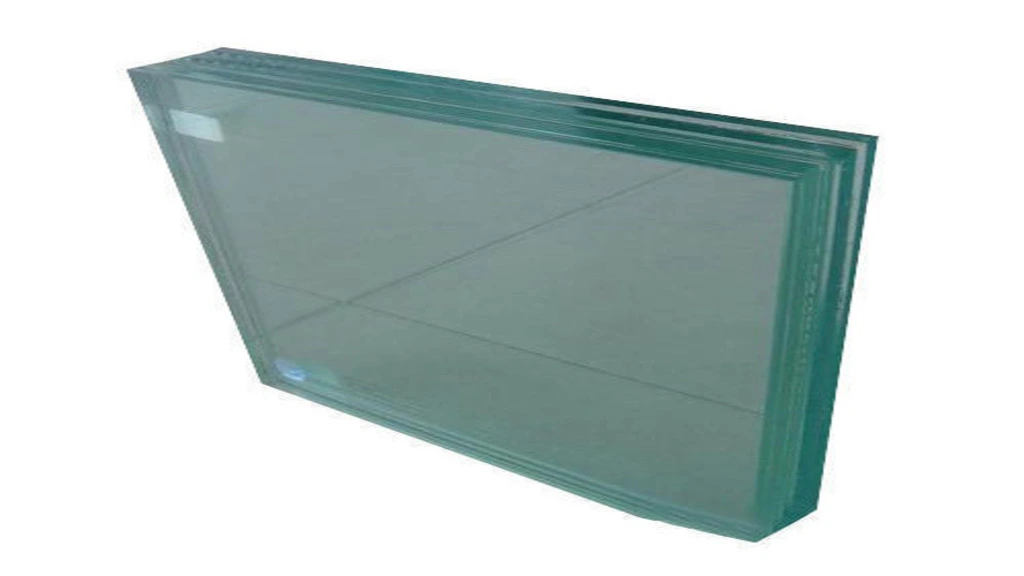

Tempered glass, a.k.a safety glass, undergoes a process of rapid heating and cooling, resulting in a product that is several times stronger than annealed glass. What sets this toughened glass railing design apart is its unique breakage pattern: upon impact, it fractures into small, dull pieces, reducing the risk of injury. This safety feature makes tempered glass an excellent choice for areas prone to accidents or requiring enhanced security.
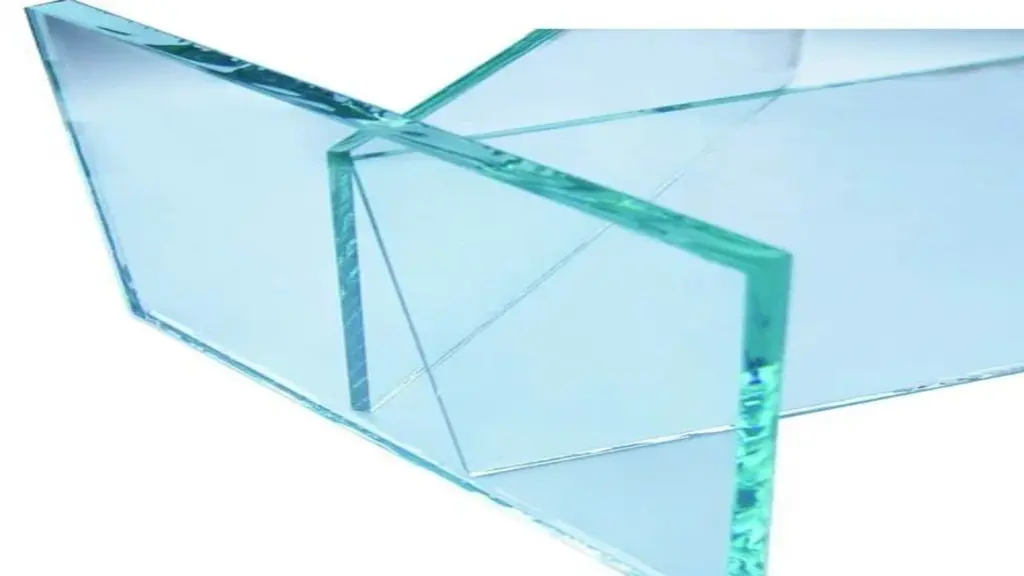

Heat soak tempered glass undergoes an additional heating process to further reinforce its strength and durability. By subjecting the glass to prolonged heat, any potential defects or impurities are identified and eliminated, ensuring maximum reliability and performance. Heat-soak tempered glass is an ideal option for applications where exceptional safety and longevity are non-negotiable.
Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded together, typically using a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer. This construction provides unparalleled safety and security, as the glass remains intact even when shattered, making it one of the best types of glass in interiors. Laminated glass is commonly used in applications requiring resistance to forced entry, such as exterior doors and windows, as well as for soundproofing and UV protection.
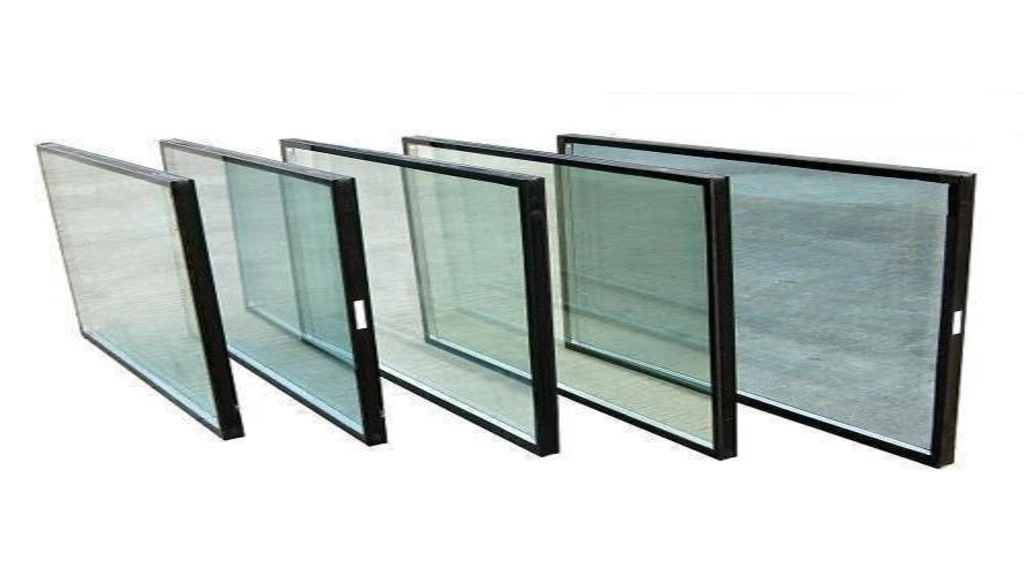

Insulated glass, a.k.a double-glazed or triple-glazed glass, features multiple panes separated by a space filled with air or inert gas, such as argon or krypton. This design provides superior thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and energy loss which makes it one of the types of glass in interiors in cold environments. Insulated glass is a popular choice for improving energy efficiency in buildings and homes, helping to lower heating and cooling costs while enhancing comfort year-round.
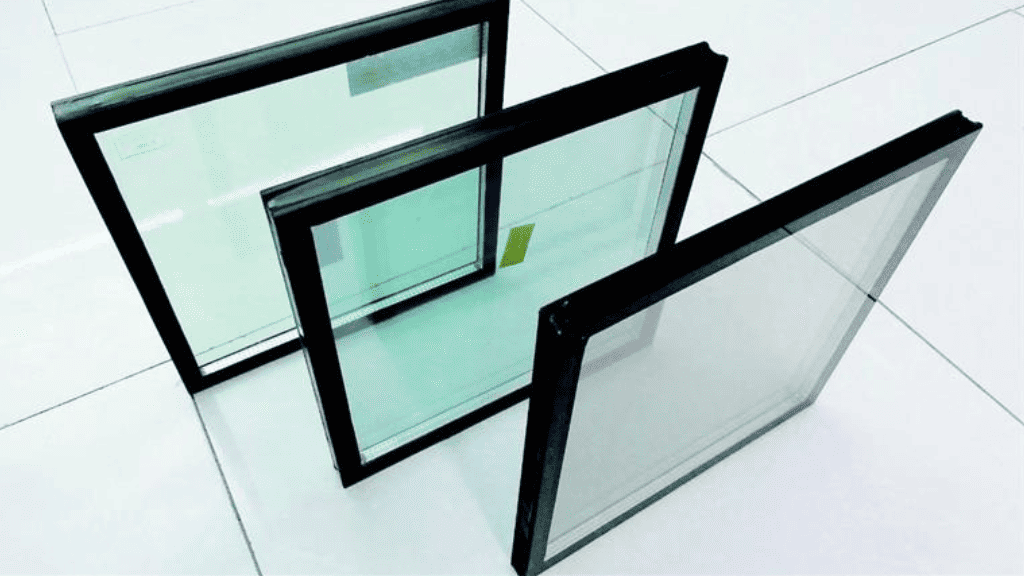

Gas-filled glass takes insulation to the next level by incorporating inert gases, such as krypton or argon, between the glass panes. These gases insulate air better, further reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency, making it one of the best types of glass used in interiors. Gas-filled glass is an excellent option for climates with extreme temperatures, providing enhanced comfort and energy savings.
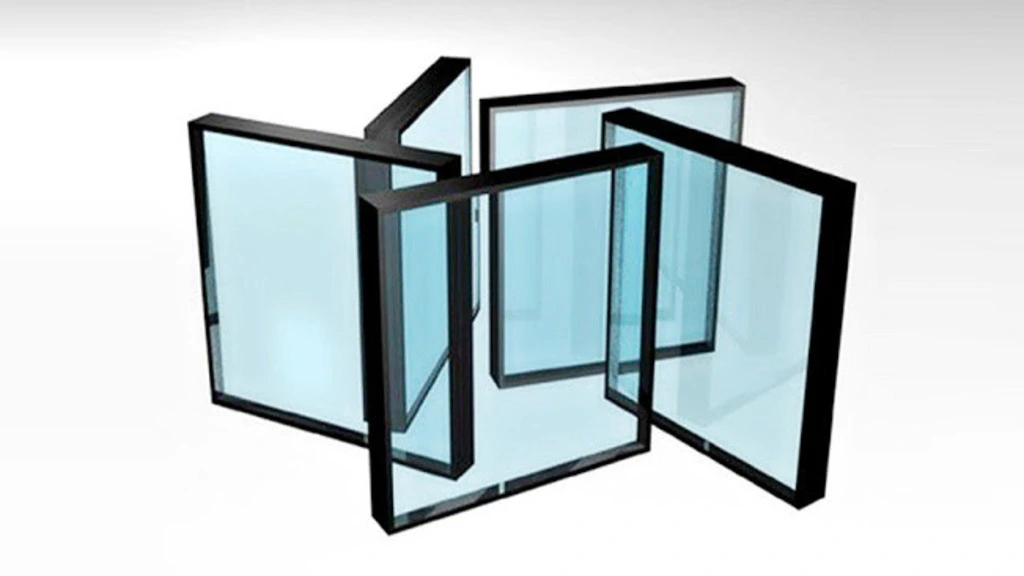

Low-emissivity or Low-E glass features a thin, transparent coating that deflect heat and at the same time allow visible light to pass through. This innovative technology helps regulate indoor temperatures by blocking heat gain in the summer and retaining heat in the winter. Low-E glass also reduces UV radiation, protecting furnishings and fabrics from fading. With its energy-saving benefits and year-round comfort, Low-E glass is a popular choice for modern homes and buildings, making it one of the best types of glass used in interiors.
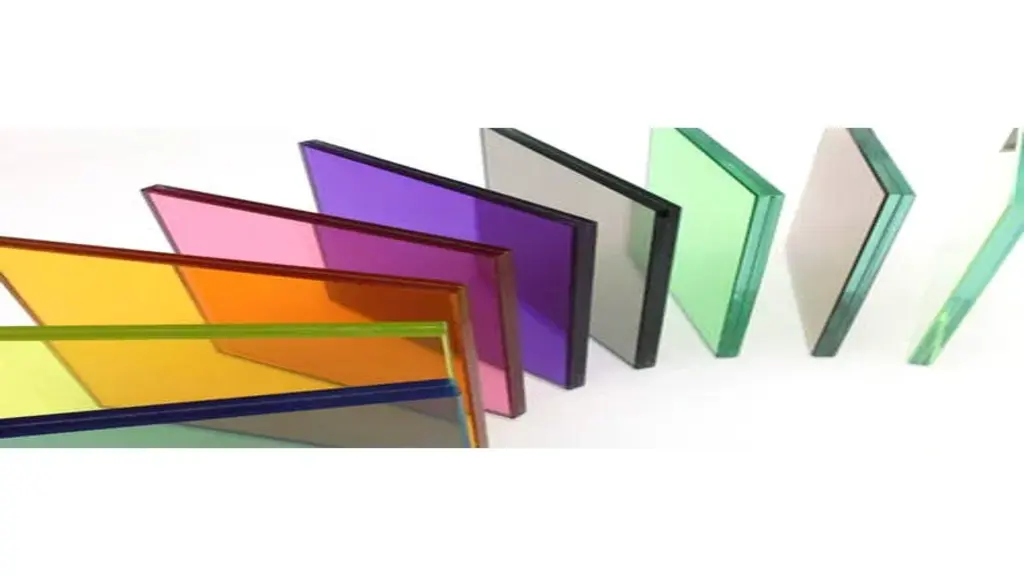

Tinted glass is infused with colorants that absorb a portion of the sun’s heat and glare, reducing the need for excessive cooling and improving comfort indoors. Available in a variety of shades, this glass design for home offers both practical benefits and aesthetic appeal, enhancing the exterior appearance of buildings while providing privacy and sun control.
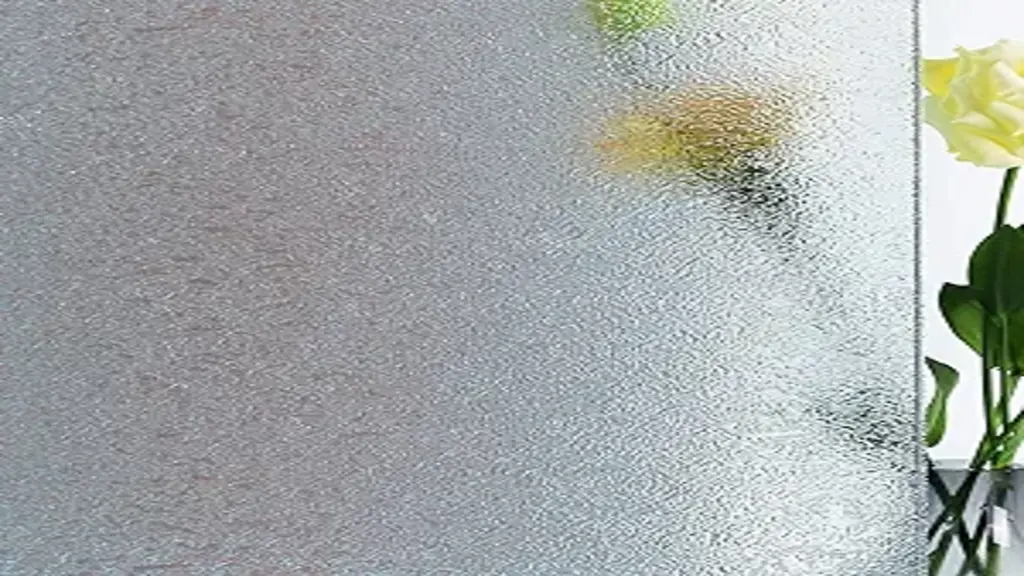

Obscured glass, whether frosted, patterned, or textured, offers privacy without sacrificing natural light. Commonly used in bathrooms, entryways, and other areas requiring discretion, this glass design for home adds character and charm to any space while maintaining functionality and practicality.
The choice of glass for your windows is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the comfort, energy efficiency, and safety of your home. By understanding the properties and applications of the various types of glasses available, you can make an informed choice that meets your specific needs and enhances the overall quality of your living space. Whether you prioritize safety, energy efficiency, or aesthetic appeal, there’s a glass option tailored to your requirements. So, take your time, explore your options, and elevate your home to new heights of style and functionality with the perfect glass for your windows.
Visit Propertygeek