
Lifts or elevators are cars pr devices that move goods and/or people vertically on a dedicated shaft that connects the different stories of a building structure. These types of lifts became a common sight in the 1850s as iron and steel structural frames started aiding the construction of taller buildings.
However, it took Elisha Otis’s safety mechanism to make the cars fall-proof. This preventive addition propelled the use of elevators or lifts into a popular trend. In most modern multi-story buildings, lifts are a means to universal access.
What are Lifts?
Lifts, also called elevators, are cars that move in a vertical shaft to carry people or even freight between different levels of a multistory structure. Most modern lifts are propelled by electric motors through a system of sheaves (pulleys) and cables with the aid of a counterweight. Here are the different types of elevator at a glance:
- Passenger lifts
- Freight or goods lift
- Hospital lifts
- Service lifts
- Capsule lifts
- Hydraulic lifts
- Roped hydraulic lifts
- Conventional hydraulic lifts
- Hole-less hydraulic lifts
- Traction lifts
- Geared traction lifts
- Gearless traction lifts
- Machine-room-less (MRL) lifts
- Vacuum (air-driven) home lifts
How Has The Law Influenced The Usage of Elevators?
Elevators became common in the US when the Americans with Disabilities Act was put forth in 1990. This legislation forbids any kind of discrimination against people with disabilities and required all three or two-storied structures to have elevators in them. This decision made it convenient for people living with disabilities to access all the floors of a multi-story building.
The first elevator in India was installed in the heritage building of Raj Bhavan in Kolkata (then Calcutta) by the Otis Elevator Company in 1892.
How Do Elevators or Lifts Work?
Elevators or lifts still use the Otis Safety System since the 1850s and have not deviated from their original purpose of transporting people or goods across multiple stories in the structure of a building.
Control systems in lifts have been altered to suit modern purposes with improved safety and speed. Usually, lifts apply about 40% of the maximum rated load and the counterweight to balance the car. Counterweights are used to reduce the weight off the motor and to keep the lift in control without affecting the cables.
To ensure strength and durability, the car is made of steel and the pulley is held in place by a shaft. This spin is regulated by steel beams placed above the car. These days, some elevators allow phone service to call for help during an emergency while others are fitted with a trap door in their ceilings as an escape route.
Let’s Read The Details of Each Type of Lifts!
1. Passenger Lifts
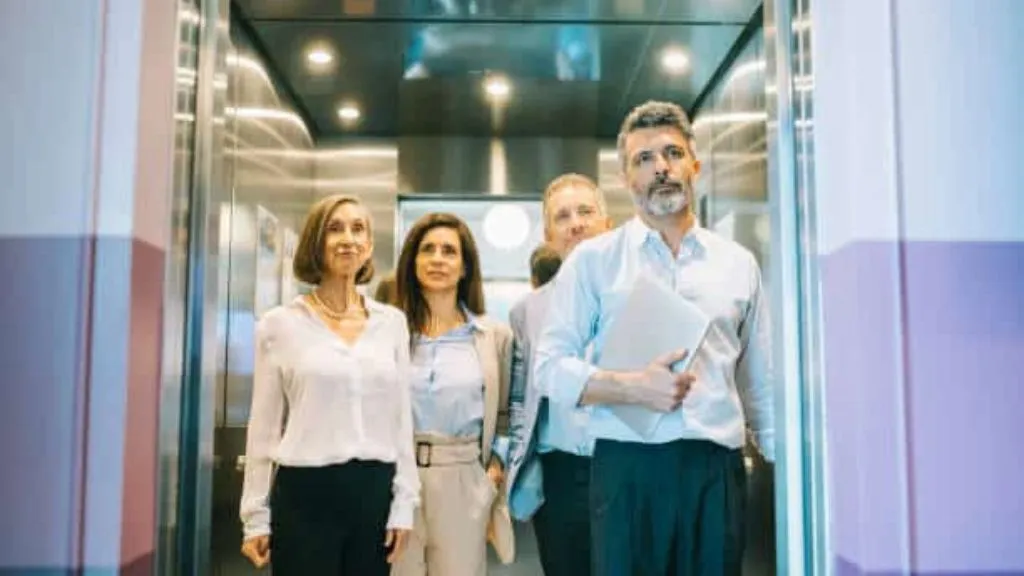

Passenger lifts are the main means of transportation in high-rise hotels, apartments, commercial complexes, offices, hospitals, buildings, etc. It is recommended that these types of lifts have a center opening door. Passenger lofts can be classified into several types depending on their rated speed and load-carrying capacity.
2. Freight or Goods Lifts
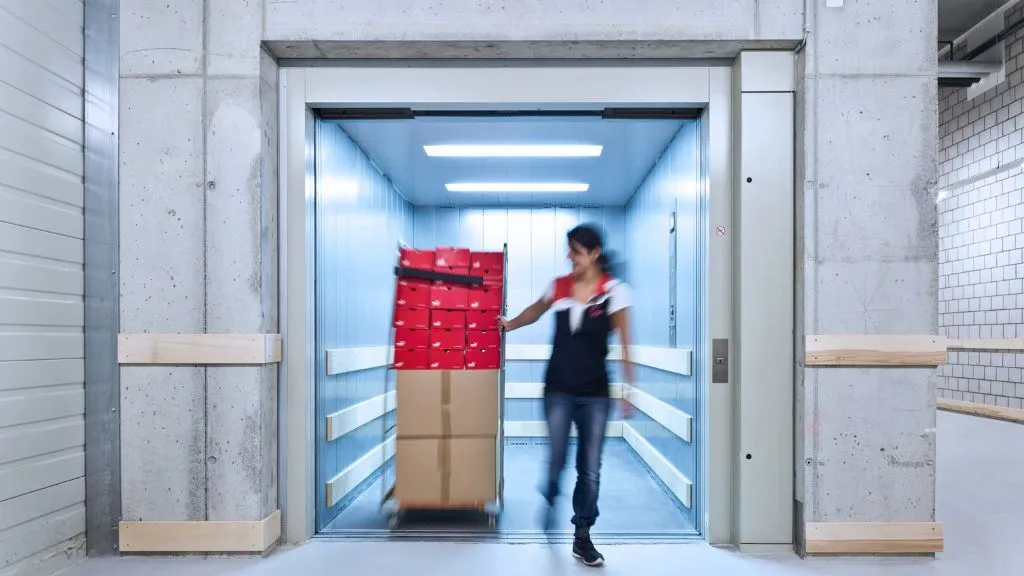

Goods or freight lifts are used for the vertical transportation of goods and/or materials. These types of lifts have a speed of 0.25m/s to 1m/s and are available in loads ranging from 500kg to 5000kg. The more the carrying capacity of the lift the less will be the recommended speed. To install freight lifts or elevators, certain factors are to be considered:
- The characteristics of the building
- The handling of the method
- The weight and size of the materials to be transported
3. Hospital Lifts
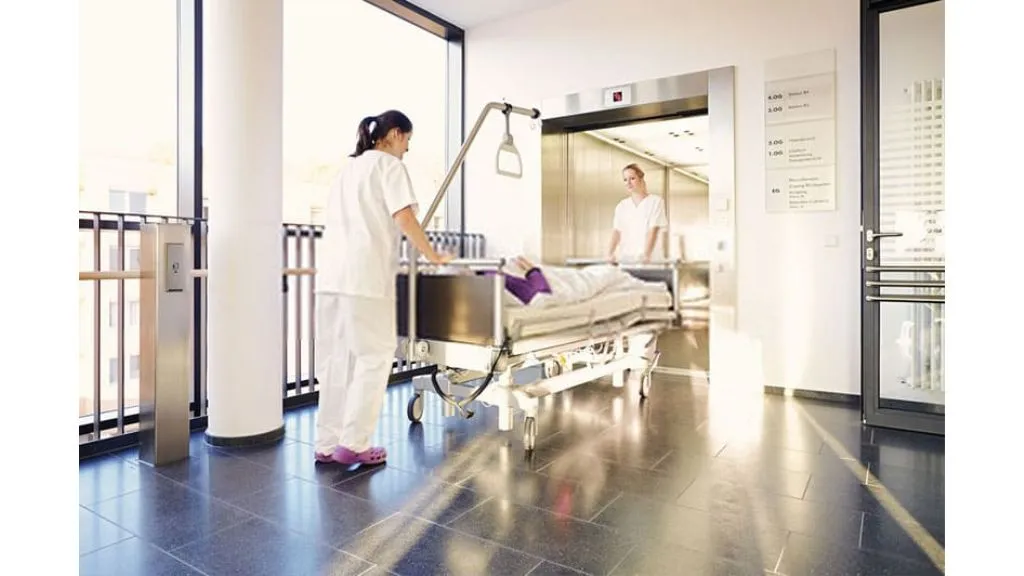
Elevators or lifts are a necessity in polyclinics, nursing homes, and hospitals as they carry stretchers and other heavy pieces of hospital equipment across different floors of the building. For small hospital buildings, a speed of 0.5 m/s is recommended. In cases of long travel, the desirable speed could be up to 1.5 m/s.
These types of lifts need to have two speed sliding doors with automatic opening/closing devices along with micro leveling. The shaft of this type of lift is situated very close to the wards and operation theatres.
4. Service Lifts
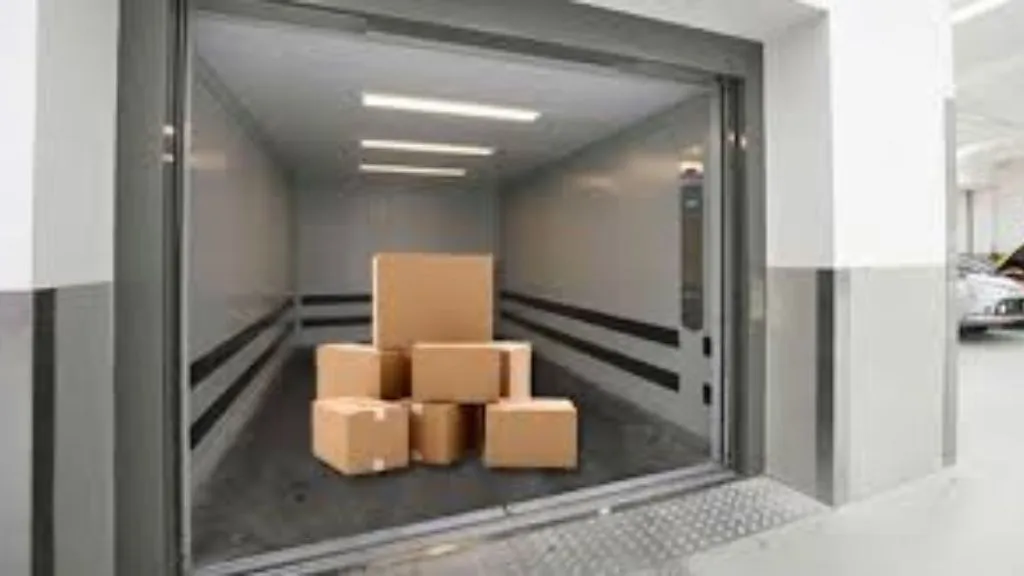

Service lifts also known as dumb waiters are slow mini-lift that handles only material transportation vertically from 100kg to 250kg with a speed of 0.25 m/s to 0.5 m/s. The number of floors to be accessed by the lift decides the control system of the lift. There are un general be two kinds of control systems:
- The call and send control system
- The multi-button control system
5. Capsule Lifts
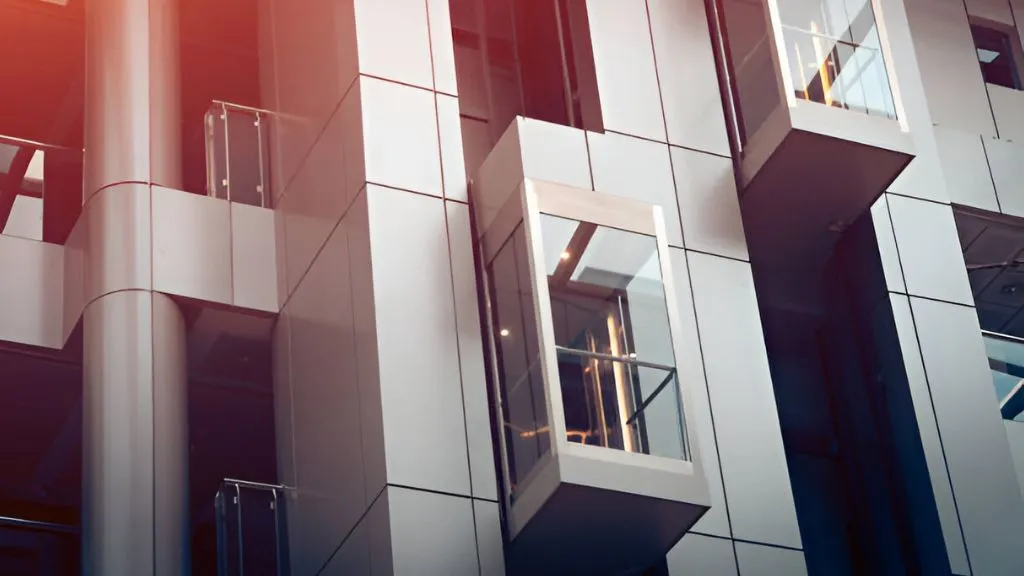

Capsule lifts or elevators are capsule-shaped lifts that usually have glass walls. They are placed in the same place as elevators but give people inside them a visual advantage. They are usually found in the exteriors of buildings, in the lobby, or at a place that enhances the look of the building as well as its elevation.
6. Hydraulic Lifts
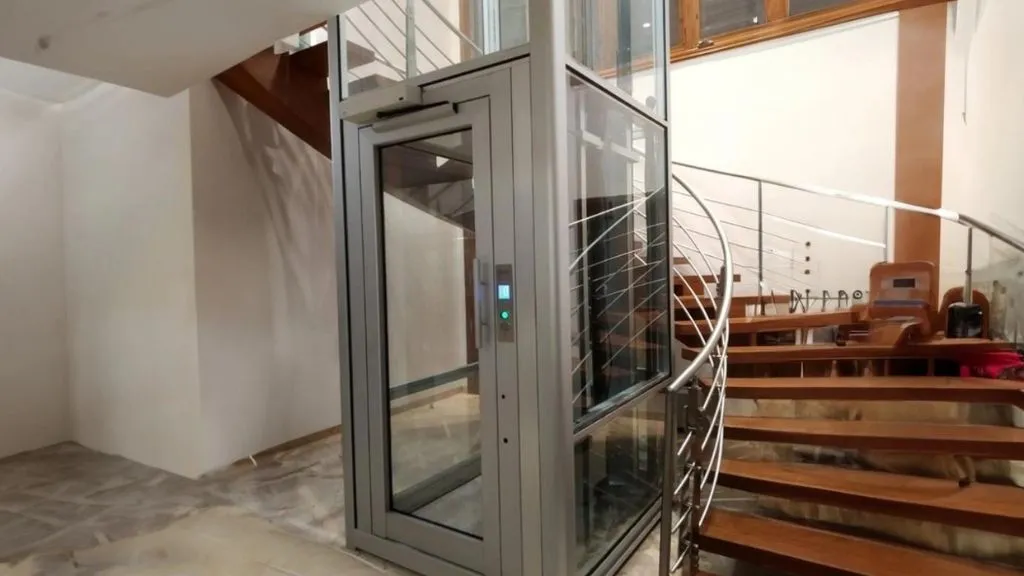

Hydraulic elevators are types of elevators that utilize the pressure of water to obtain motion. It could also use oil instead of water. These elevators are supported by a bottom-placed piston whose purpose is to push the elevator up. An electric motor is used to force hydraulic fluid down the piston. When the car comes down, the valve discharges hydraulic fluid from the piston.
These lifts tend to use more energy as they work with electric motors that work against gravity. You need to keep hydraulic fluids in regular check as even a small leak could be catastrophic. Here are the features of a hydraulic lift:
- It is the perfect solution in old buildings where there is no provision for lofts.
- Hydraulic lifts are ideal in low-rise buildings with their smooth acceleration and moderate speed. The maximum travel range is 12 meters whereas the speed ranges from 0.1 m/s to 1 m/s.
- These type of lifts does not need a machine room. A small room of 50 sq. ft. will suffice.
6.1. Roped Hydraulic Lifts
- This type of lift makes use of both a piston and ropes that enhances the car’s motion. The maximum distance that a roped hydraulic lift for home can travel is about 60 feet.
6.2. Conventional Hydraulic Lifts
- These types of lifts are designed with an elevator pit and come in sheaves extending underneath the floor of the pit. When the elevator comes down, the pit supports a retracting prison. Sometimes, these lifts require a shallow hole below the pit to accept a collapsing telescoping piston when the car comes down. The approximate distance that conventional hydraulic elevators travel is 60 feet.
6.3. Hole-less Hydraulic Lifts
- This type of lift is similar to the conventional one but does not need a sheave or a hole below the pit. The base of the pit of hole-less elevators has telescoping pistons that allow the car to travel a distance of 50 feet.
- Those lifts with non-telescoping pistons travel only up to 20 feet.
- These lifts are quite popular because of their affordability and lower maintenance costs
7. Traction Lifts
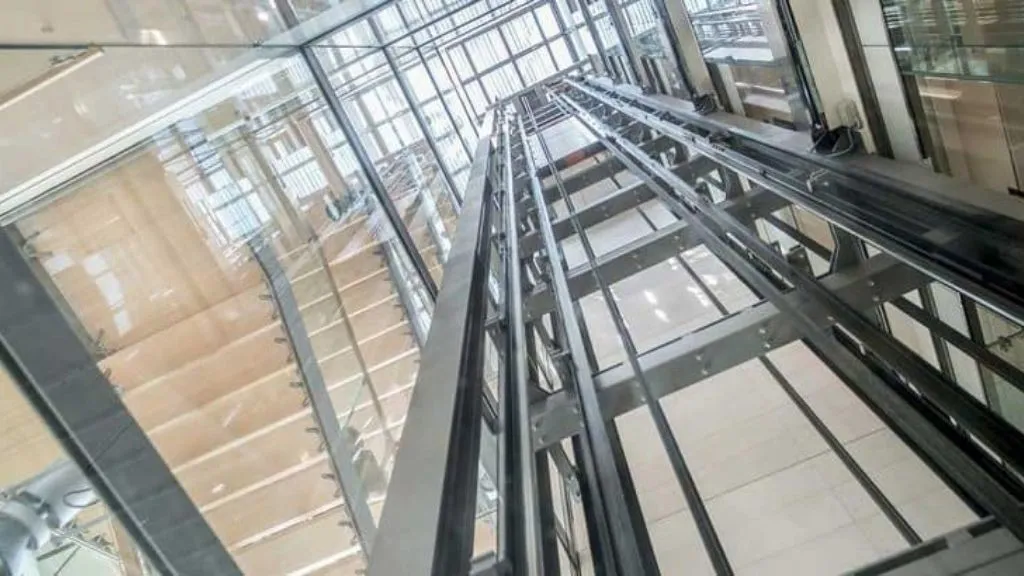

Traction elevators or lifts have ropes passing over a wheel that is attached to an electric motor. This motor is located above the shaft of the elevator. The main purpose of these ropes is to lower and raise the car and are applicable in both high and mid-rise applications. These lifts can travel much faster than hydraulic lifts.
Similar to other elevators or lifts, traction elevators use a counterweight to eliminate the weight of the car and its occupants making it easier for the motor to move the load. Here are its two types:
7.1. Geared Traction Lift
Geared traction lifts or elevators java a motor with a gearbox attached to it whose main purpose is to power the wheel that moves the ropes. These types of lifts have a speed of 500 feet per minute and the maximum distance that they can travel is 250 feet.
7.2. Gearless Traction Lift
Gearless traction lifts have no gear, as the name suggests which is also the reason they can move as fast as 2000 feet per minute with a maximum distance of 2000 feet. These are the perfect choice of elevators for skyscrapers.
8. Machine-room-less (MRL) Lifts
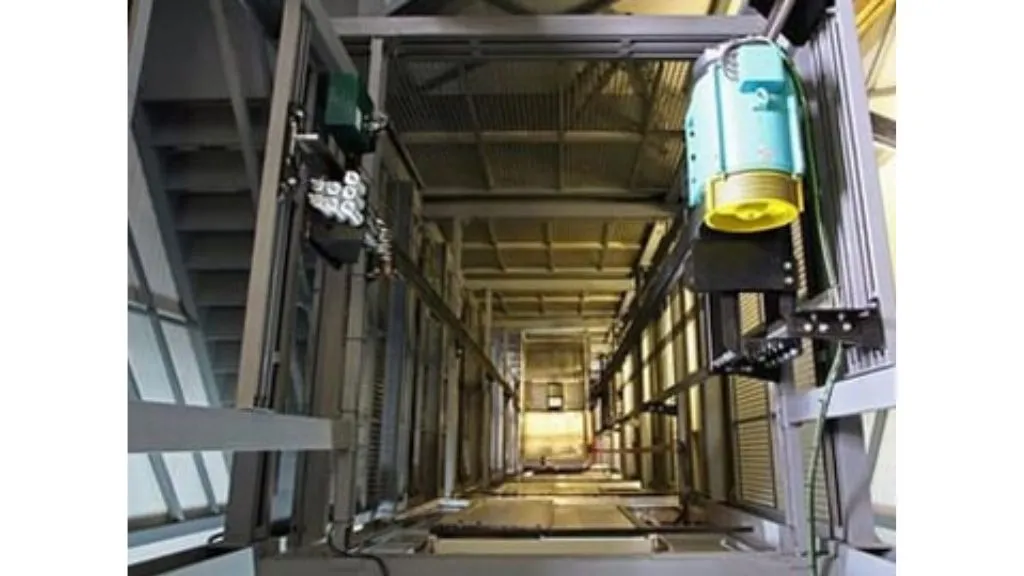

Typically, lifts are designed with a machine room above the elevator shaft but this type of lift has a machine fitted in the override space. It can only be accessed via the top of the elevator car as and when maintenance is demanded.
These lifts travel only a distance of 250 feet with a speed of 500 feet per minute. MRL lifts have gained popularity over time with mid-rise buildings because of their low energy consumption and less space occupancy during construction.
9. Vacuum (Air-driven) Home Lift
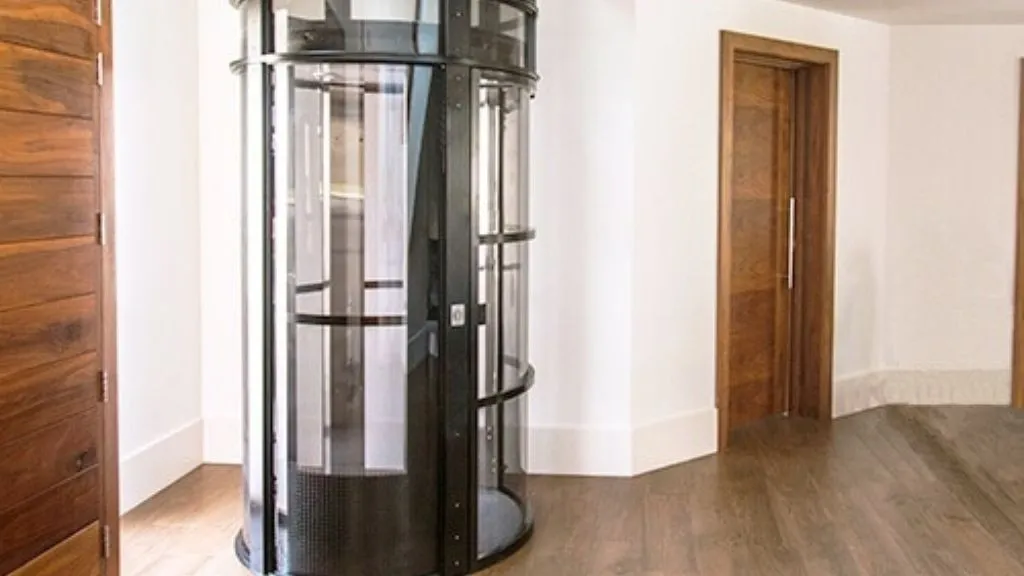

Vacuum lifts were introduced in 2005. They do not use a pulley or cable system but the natural laws of physics. These lifts are constructed with aluminum and polycarbonate materials and are sealed vacuum tubes. The air above and beneath the car helps in moving it up and down.
While moving upwards, the lift system lowers the pressure above the car which forces the air pressure below the car to push it upwards. On the other hand, when the car goes down, the air pressure below the car is minimized forcing the tube to go down.
Vacuum elevators are types of lifts for homes as they have three models ranging from a three-passenger wheelchair-accessible model to a single passenger model.
The Bottom Line: Different Types of Lifts for Buildings
High-rise building structures need to have lofts to have accessibility to all floors, more so if it is a hospital, office, or other public buildings. Even residential buildings need elevators to make all floors accessible to people of all ages. Elevators or lofts are found very commonly in public buildings so make them universally accessible to the public. Here we have brought you the different types of elevator for buildings that are quite common.
How To Clean A Lift?
Cleaning a lift (elevator) is essential to maintain hygiene and ensure a safe and pleasant experience for its users. Here are the general steps to clean a lift:
- Gather Cleaning Supplies:
- All-purpose cleaner or disinfectant spray
- Microfiber cloths or disposable wipes
- Glass cleaner for mirrors and glass panels, if applicable
- Bucket and mop for cleaning the lift floor, if necessary
- Broom or handheld vacuum cleaner for removing debris
- Rubber gloves and face mask for protection
- Remove Debris:
- Sweep the lift floor or use a handheld vacuum cleaner to remove dirt, dust, and debris. Pay attention to corners and edges where dirt often accumulates.
- Clean the Interior:
- Spray all-purpose cleaner or disinfectant on a microfiber cloth or disposable wipe.
- Wipe down the walls, handrails, buttons, and any other surfaces inside the lift. Ensure you cover all frequently touched areas thoroughly.
- Use glass cleaner to clean mirrors and glass panels, if the lift has them.
- Clean the Floor:
- If the lift has a hard floor, mop it using a mixture of mild soap and water. Avoid using excessive water to prevent damage to the lift floor.
- For lifts with carpeted floors, vacuum the carpet thoroughly. If there are stains, spot-clean them with a suitable carpet cleaner.
- Disinfect High-Touch Surfaces:
- Focus on disinfecting high-touch surfaces such as buttons, handrails, and interior door handles. Use disinfectant wipes or a cloth soaked in disinfectant to ensure proper sanitization.
- Clean the Exterior:
- If the lift has glass panels or windows on the exterior, clean them using the appropriate glass cleaner and a clean cloth.
- Wipe down the outer surface of the lift doors and frames, removing any visible dirt or smudges.
- Polish and Shine (Optional):
- Consider using a stainless steel cleaner or metal polish on stainless steel surfaces inside the lift, like handrails or door frames, to maintain their shine.
- Replace Trash Bags (if applicable):
- If there’s a trash bin inside the lift, replace the trash bag with a new one and ensure proper disposal of the waste.
- Ventilation:
- Ensure the lift is well-ventilated during and after cleaning to help any cleaning fumes dissipate.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Establish a regular cleaning schedule to ensure the lift stays clean and inviting for users. Regular maintenance also prolongs the life of lift components.
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning and maintenance, and use appropriate cleaning agents to avoid damage to lift surfaces. Safety should be a priority, so be cautious when cleaning in and around moving parts.






