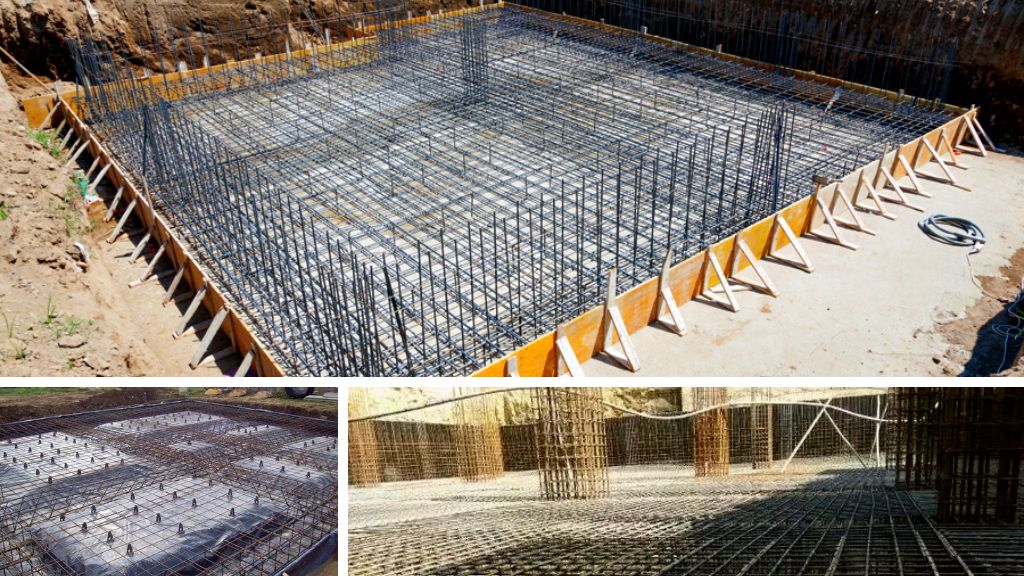

In construction, the foundation plays a pivotal role in ensuring the strength and stability of a structure. One of the most reliable choices for foundations is the raft foundation, also known as a mat foundation. This foundation is especially beneficial for buildings with heavy loads or in areas with weak soil, as it evenly distributes the weight across a large surface area.
Whether building a residential home, a commercial building, or a skyscraper, selecting the appropriate raft foundation is essential for long-term structural integrity. In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of raft foundations, their advantages, and how they function in civil engineering projects, supported by a raft foundation diagram for better understanding.
What is Raft Foundation?
A raft foundation is a large, solid slab of reinforced concrete that spans the entire footprint of a building. It is designed to spread the structure’s weight evenly over a large area, reducing pressure on the soil. Unlike isolated footings that support individual columns, raft foundations provide a continuous base, ensuring stability even on weak or compressible soil.
- Purpose of a Raft Foundation: It acts as a single platform for distributing loads from multiple columns or walls.
- Appearance and Design: A typical raft foundation diagram shows a flat, thick slab that includes reinforcement bars, often paired with beams for added support.
This foundation type is commonly used in areas where the soil’s load-bearing capacity is low or when the structure requires added stability.
Different Types of Raft Foundations and Their Functions
In civil engineering, a raft foundation is a large concrete slab that supports a building, spreading the weight evenly across a large area. This foundation is beneficial in conditions where the soil is weak or when the building is large, distributing the load to prevent settlement issues.
Various types of raft foundations are used depending on the project’s size, soil conditions, and load requirements. Let’s explore these types in detail, focusing on their unique functions and applications.
1. Solid Slab Raft Foundation
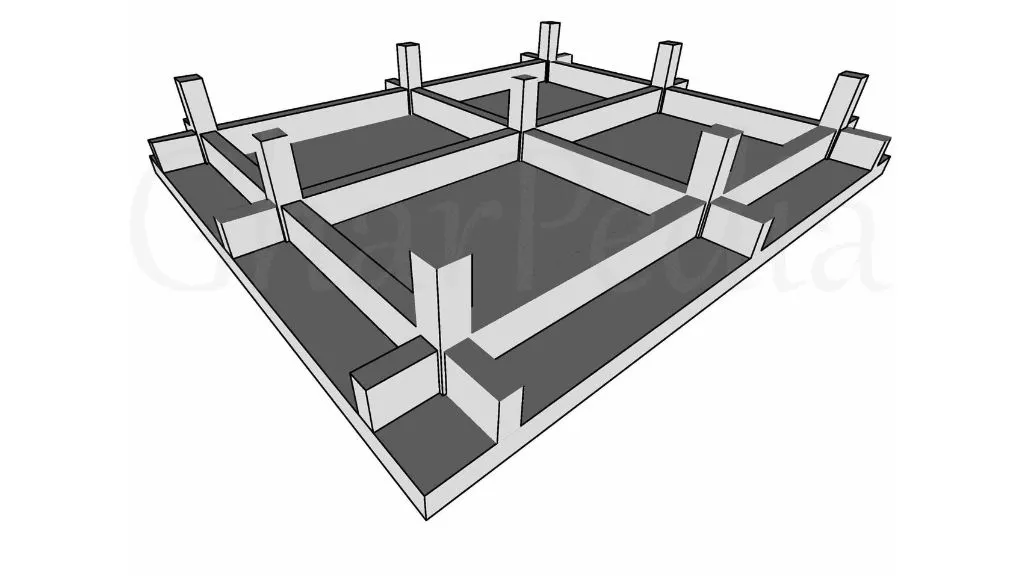
A solid slab raft foundation is the most basic type of raft foundation. As the name suggests, it consists of a solid, continuous concrete slab that covers the entire area of the building’s footprint. This foundation type is commonly used for small and medium-sized structures.
- Functionality: The solid slab evenly distributes the load from the structure across the soil, minimizing the chances of uneven settlement. It provides basic structural support without any added reinforcement.
- Application: Ideal for light- to medium-weight structures, such as tiny residential homes or storage warehouses.
This type is ideal for stable soil conditions and lighter buildings that do not exert excessive weight on the foundation.
2. Beam and Slab Raft Foundation
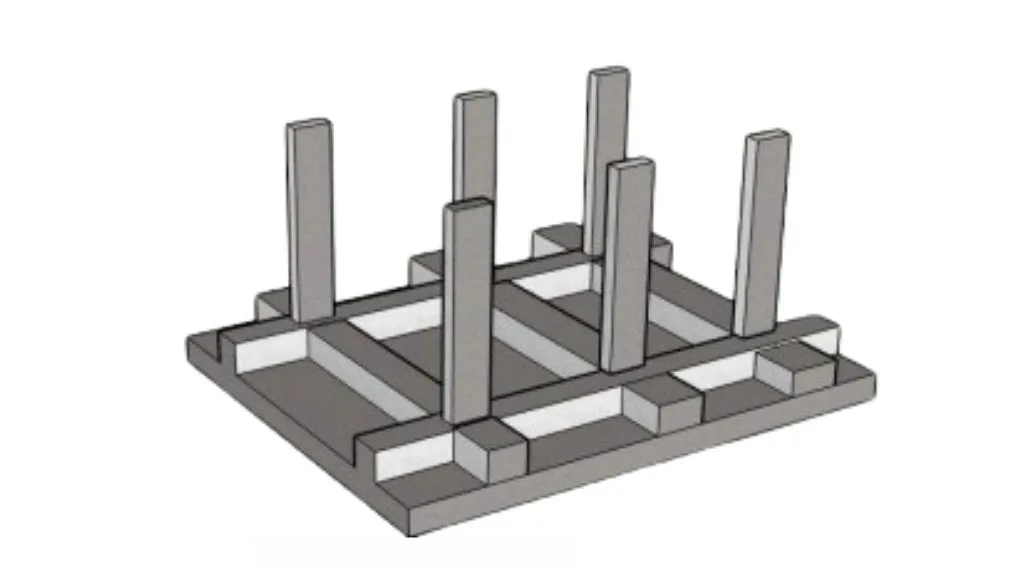
A beam and slab raft foundation combines a solid concrete with reinforced concrete beams. The beams run in both directions, providing additional support and enhancing the foundation’s strength. This raft foundation type is beneficial when the soil is weak or uneven.
- Functionality: The concrete beams help improve the raft foundation’s stiffness, making it better equipped to handle heavier loads. This raft foundation ensures uniform load distribution, making it a reliable choice for buildings on soft or compressible soil.
- Application: Commonly used for medium- to large-sized commercial buildings, industrial facilities, or multi-story apartments that require extra support.
The beam and slab raft foundation provides the necessary stability for structures with varying load requirements or where the ground conditions aren’t uniform.
3. Cellular Raft Foundation (Waffle Raft Foundation)
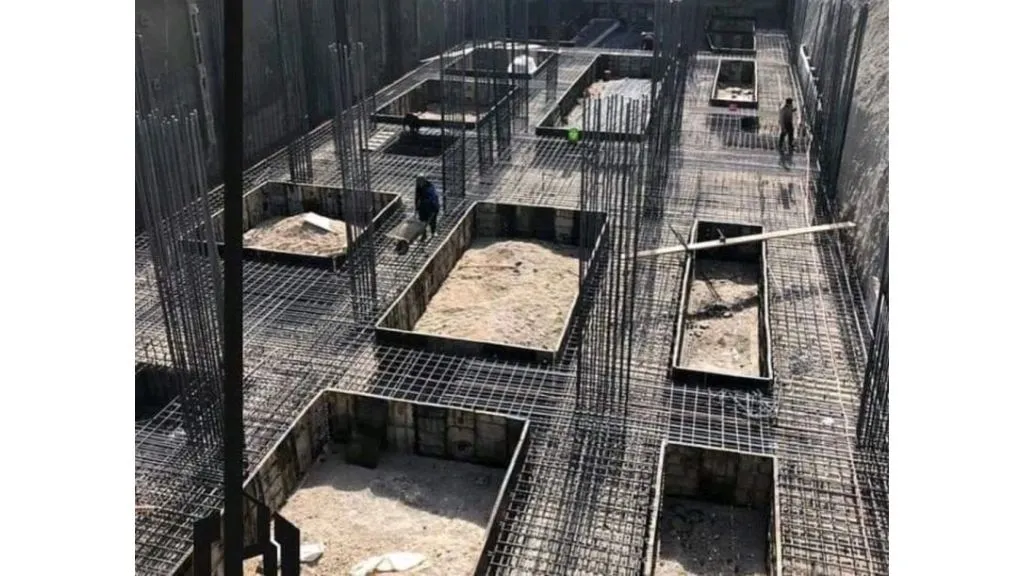

A cellular raft foundation, or a waffle raft foundation, is designed with a grid of recessed cells in the concrete slab. These grid-like voids reduce the amount of concrete needed while maintaining the foundation’s overall strength.
- Functionality: The cellular structure helps reduce the weight of the foundation while ensuring sufficient strength to support large buildings. The voids also enhance the foundation’s stiffness, making it suitable for larger projects.
- Application: This type is often used in large-scale construction projects such as stadiums, high-rise buildings, or large commercial complexes requiring high load-bearing capacity.
The waffle raft foundation is a great choice when a large area needs to be supported but with reduced material usage, making it cost-effective while maintaining strength.
4. Piled Raft Foundation
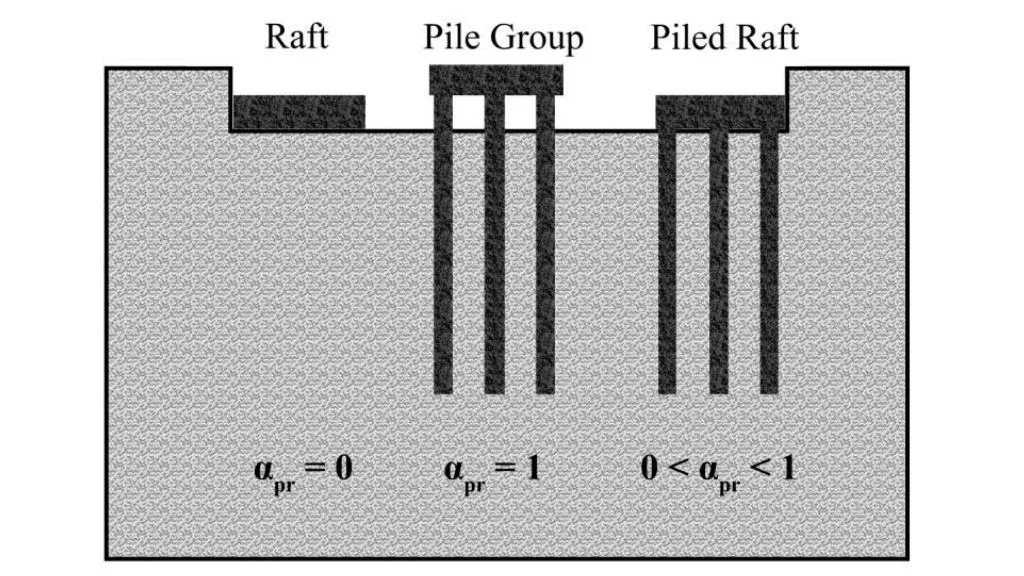
A piled raft foundation combines a traditional raft foundation with deep piles reaching firmer soil layers. This type of foundation is especially beneficial in areas where the soil near the surface is weak or unstable.
- Functionality: The piles provide additional support by transferring part of the load to deeper, more stable soil layers, while the raft distributes the load evenly across the surface. This hybrid system ensures maximum stability for large or heavy structures.
- Application: Skyscrapers, bridges, and industrial plants are typical applications for this type of raft foundation, where extreme weight and load-bearing are required.
By reaching deeper into the ground, piled raft foundations ensure that buildings remain stable even in challenging soil conditions, offering an effective solution for large-scale projects.
5. Floating Raft Foundation
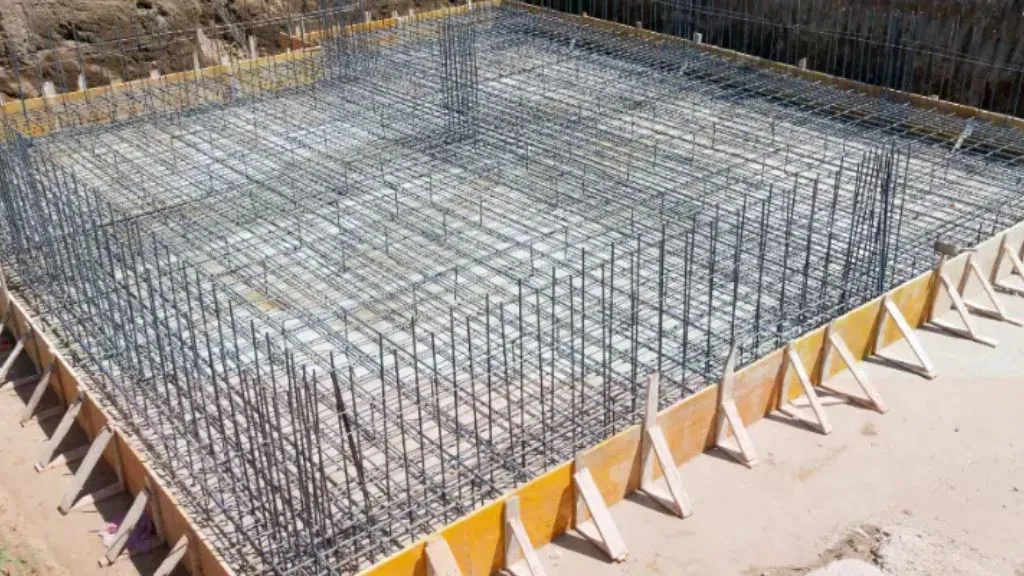

A floating raft foundation is designed in such a way that the weight of the building is counteracted by the weight of the soil that is excavated beneath the structure. In this setup, the foundation “floats” on the soil, balancing the weight of the building and preventing excessive pressure on the ground.
- Functionality: This raft foundation reduces the pressure exerted on the soil by evenly distributing the building’s weight across a larger surface area. It is advantageous when the soil is compressible or prone to shifting.
- Application: Ideal for projects in flood-prone areas, marshlands, or regions with soft and compressible soils.
Floating raft foundations help in maintaining structural stability, especially in conditions where traditional foundations fail to offer sufficient support.
6. Flexible Raft Foundation
A flexible raft foundation is designed to adapt to varying soil conditions and ground movements. It dynamically redistributes loads as the soil beneath it shifts or compresses. This makes it suitable for buildings in regions prone to earthquakes or ground settlement.
- Functionality: The flexibility of this raft foundation ensures that it can accommodate minor ground movements without causing damage to the structure. This prevents the foundation from cracking or tilting as the ground below shifts.
- Application: Commonly used in earthquake-prone zones or areas where the soil may not be entirely stable over time.
Functions of a Raft Foundation
- Distributes Load Evenly
Raft foundations are designed to evenly distribute the weight of a building across the soil. This reduces pressure on specific points, minimizing the risk of differential settlement. Such settlement, often caused by uneven weight distribution, can lead to structural damage, especially in tall or heavy buildings.
- Key Benefit: Ensures stability by avoiding stress concentration in certain areas.
- Ideal Use: High-rise structures, industrial complexes, and multi-story buildings.
- Supports Weak Soil
In areas with poor soil conditions, like clay or silt, raft foundations provide much-needed stability by spreading the load over a larger area. This reduces soil compression and prevents sinking, making these foundations particularly useful in regions with low soil-bearing capacity.
- Key Benefit: Improves building stability in challenging soil conditions.
- Application Example: Urban areas, flood-prone zones, or reclaimed lands.
- Prevents Settlement
By covering a broad footprint, raft foundations help in preventing uneven settlement of the structure. This reduces the risk of cracks, tilting, or damage caused by soil compression under the building’s weight.
- Key Benefit: Maintains structural integrity by counteracting soil movements.
- Construction Use: Residential homes, factories, and infrastructure projects.
- Cost-Effective Solution
Raft foundations are often more economical than other deep foundation methods. They require less excavation and use fewer materials, making them a practical choice for structures covering a wide area. Despite their simplicity, they offer robust support, especially for buildings with moderate to heavy loads.
- Key Benefit: Reduces construction costs without compromising on safety.
- Best Suited For: Warehouses, commercial spaces, and small-to-medium-sized buildings.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Raft Foundation for Construction
The soil at the construction site is one of the primary factors influencing the choice of raft foundation. The soil’s load-bearing capacity and uniformity determine which type of foundation is most suitable.
1. Soil Type
- Weak Soil: In areas where the soil is soft, clayey, or has poor load-bearing capacity, options like piled raft foundations are preferred. These foundations use piles to transfer the load to deeper, more stable soil layers, reducing settlement risks. Floating raft foundations are also ideal for weak soils, as they balance the building’s weight with the soil pressure.
- Uniform Soil: For sites with stable and consistent soil, simpler options like solid slab or beam and slab raft foundations work effectively. These are cost-efficient and provide even load distribution across the structure.
2. Load Requirements
The type, intensity, and distribution of loads imposed by the building significantly influence the selection of a raft foundation.
- Heavy Loads: Structures such as commercial complexes, industrial plants, or multi-story buildings often require beam and slab raft foundations for added strength. In cases of extremely heavy loads, piled raft foundations combine the benefits of a standard raft with the support of deep piles to prevent excessive settlement.
- Dynamic Loads: Facilities like factories or power plants that generate vibrations from machinery require cellular raft foundations (waffle rafts). The grid-like structure of these foundations enhances stiffness and minimizes vibrations, ensuring long-term stability.
3. Cost Implications
Budget constraints are an integral part of the decision-making process. The cost of the foundation is influenced by the type of materials, excavation depth, and reinforcement requirements.
- Affordable Options: For small-scale residential or light commercial projects, solid slab raft foundations are an economical solution. They require minimal excavation and use fewer materials compared to other types.
- Premium Solutions: For projects involving complex loads or weak soil conditions, piled raft foundations or beam and slab foundations are necessary. While these options are costlier, they provide unparalleled support and durability, justifying the higher expense in challenging environments.
4. Environmental Factors
The local environmental conditions, such as the water table level and seismic activity, are crucial considerations in raft foundation design.
- Water Table Levels: High water table regions or flood-prone areas often benefit from floating raft foundations. These foundations “float” on the soil, reducing the stress on the ground and preventing water-related structural issues.
- Seismic Activity: For construction in earthquake-prone areas, flexible raft foundations are ideal. These are designed to adjust dynamically to ground movements, preventing stress concentrations and structural damage during seismic events.
Applications of Raft Foundation in Civil Engineering
Raft foundations are a cornerstone of civil engineering, offering stability and versatility across a wide range of construction projects. Below are the key applications explained in detail:
1. Residential Buildings
Raft foundations are a popular choice for low-rise residential buildings, especially in areas with weak or compressible soil.
- Stability: They distribute the load of the structure evenly, reducing the risk of uneven settlement.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For smaller homes, solid slab rafts offer a budget-friendly solution compared to other foundation types.
- Durability: They ensure the longevity of the structure, even in regions prone to soil shrinkage or swelling.
2. Commercial Structures
Large commercial buildings, such as shopping malls and office complexes, benefit from the strength and adaptability of raft foundations.
- Heavy Load Handling: Beam and slab raft foundations are designed to manage the significant weight of these structures.
- Support for Multi-Storey Buildings: They provide a stable base, minimizing the risks of structural cracks or tilting.
3. Industrial Facilities
Factories and manufacturing units require foundations that can handle heavy equipment and vibrations.
- Vibration Absorption: Cellular raft foundations are particularly effective in reducing the impact of machinery vibrations.
- Long-Term Performance: They ensure structural stability, even under dynamic loads generated by industrial operations.
4. Infrastructure Projects
Critical infrastructure like bridges, stadiums, and dams relies heavily on raft foundations.
- Strong Base: Piled raft foundations are used to transfer the load to deeper soil layers, ensuring maximum stability.
- Adaptability: Floating rafts are suitable for flood-prone or compressible terrains, making them essential for infrastructure projects in challenging environments.
Conclusion
A raft foundation is a versatile and efficient solution for various construction challenges. By understanding the types of raft foundations, their functions, and their practical applications, engineers and builders can make informed decisions to ensure structural safety and longevity.
With options like piled rafts for heavy loads or cellular rafts for cost-effective design, there’s a suitable foundation type for every project. Careful consideration of soil type, load requirements, cost, and environmental factors ensures the foundation’s success and durability in any construction scenario.






