
Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is a key concept in real estate and urban planning that helps determine the maximum allowable built-up area on a given plot of land. It is the ratio of the total floor area of a building to the area of the land on which it is built.
FAR plays a significant role in controlling the density of development, ensuring optimal land use, and maintaining balance in urban environments. In this article, we’ll explore the meaning of FAR, how it’s calculated, its importance, and how it influences construction and urban development.
How To Calculate Floor Area Ratio?
To understand the floor area ratio, let’s understand the concept of structure limit capacity. All Indian states are of different sizes, some huge like Bombay and some relatively small like Patna.
Now, by virtue of variable available land area, each city’s capacity for housing also increases or decreases based on the availability of land– which means that each city has a limited capacity.
Now, as per the available space or land area, buildings in each city are recommended to not put any additional stress beyond a ‘safe load’ factor and that, in other words, is called the floor area ratio or FAR.
To put it in one line: The floor area ratio can be understood as the relationship between the total usable floor area permitted by the building and the total area of the lot on which the building stands. FAR is often cited by authorities as one of the regulations in city planning along with the building-to-land ratio.
What Is The Floor Area Ratio Formula?
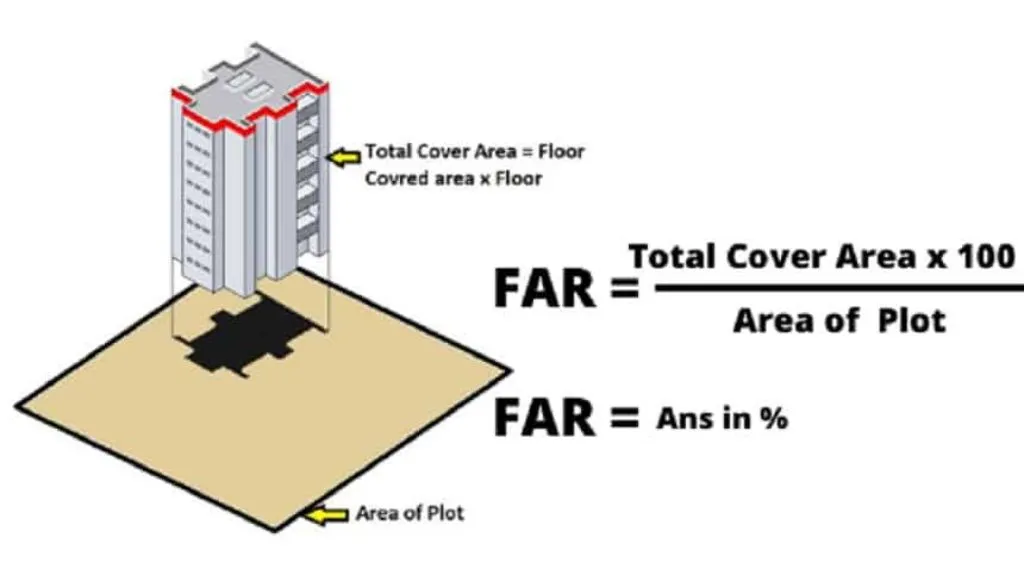
FAR is calculated by the following formula-
The total covered area of all floors divided by the total plot area
Why Is Floor Area Ratio Different In Different Cities?
The floor area ratio or FAR may not only vary from city to city but also from one locality to another, depending upon the nature of the structure, such as industrial, residential, commercial, or agricultural. FAR is variable because the population dynamics, organic growth patterns, and construction activities vary from the nature of the land or space where a building is placed.
This means buildings with different floor counts located in different cities could have the same value for the floor area.
Why Is Floor Area Ratio Important?
FAR is one of the most important factors in terms of the price of a building and is essentially the determining factor for development in any country. A low floor area ratio is considered a blockage for construction and hence, for growth or development.
A high floor area, on the other hand, means double the market value as an increased floor area ratio means a higher scope for a builder to complete more building projects resulting in greater sales, lower expenditures per project, greater supply, and hence, better overall growth and development.
From a buyer’s point of view, a higher floor area ratio means a denser building or area of residence, or in other words, more residents sharing common amenities like lifts, pools, clubs, and even electricity and water.
Floor Area Ratio and House Completion Certificate
It must be noted that the municipal authorities may assign a floor area ratio of x to the builder, however, post assignment, it is the builder’s responsibility to undertake the construction within the assigned ratio.
It is only once the construction is complete and the builder applies for a completion certificate that authorities cross-check the guidelines that were adhered to.
In case the builder violates the FAR, the authorities will have the complete right to not issue the completion certificate, which, in other words, renders the property illegal and useless. This is why it is recommended to invest in a property only after reviewing its completion certificate and save yourself from scams.
Final Thoughts: Floor Area Ratio vs Lot Coverage
Before we say goodbye, here’s a most commonly confused concept as a final explanation: Floor Area Ratio (FAR) and Lot coverage.
- The ratio calculates the overall size of the building relative to the lot
- Lot coverage accounts for the size of the buildings and structures
In other words, the lot coverage ratio includes ancillary structures of a building like a clubhouse, parking area, swimming pools, and sheds whereas the floor area ratio accounts for the floor area of a building, not the building’s footprint.






