
Selecting the appropriate slab type for a construction project is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and longevity. Incorrect slab selection can result in inadequate support, poor durability, and increased maintenance costs.
This article explores 20 different types of slabs used in construction, each with unique characteristics and applications, empowering builders and architects to make informed decisions that optimize structural performance and minimize long-term expenses.
20 Different Types of Slabs Used in Construction
1. One-way Slab
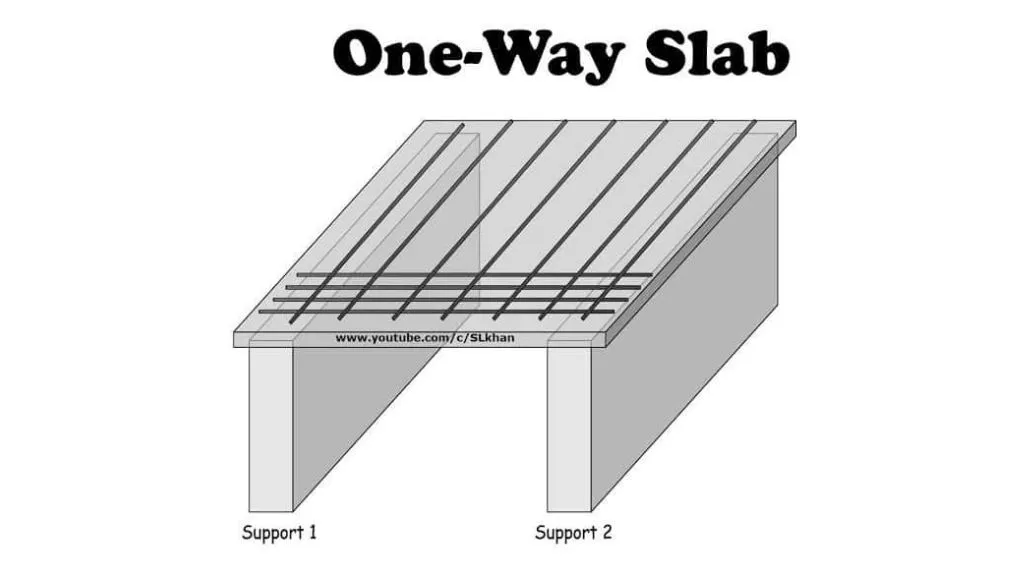
A one-way slab is a structural element designed to carry loads predominantly in one direction. The reinforcement is placed in the direction perpendicular to the span, such as along beams or walls. These types of slabs are commonly used in situations where the loads primarily act in one direction, such as in corridors or rectangular-shaped rooms.
2. Two-way Slab

Two-way slabs are specifically engineered to bear loads in two perpendicular directions. Reinforcement is strategically placed in both directions, forming a grid-like pattern. These types of slabs are ideal for spacious floor areas, as they effectively distribute loads in multiple directions, providing superior structural stability and support. With their ability to handle substantial loads, two-way slabs offer a reliable solution for projects that require robust load-bearing capabilities and enhanced structural integrity.
Also Read: Difference between one-way slab and two-way slab
3. Flat Slab
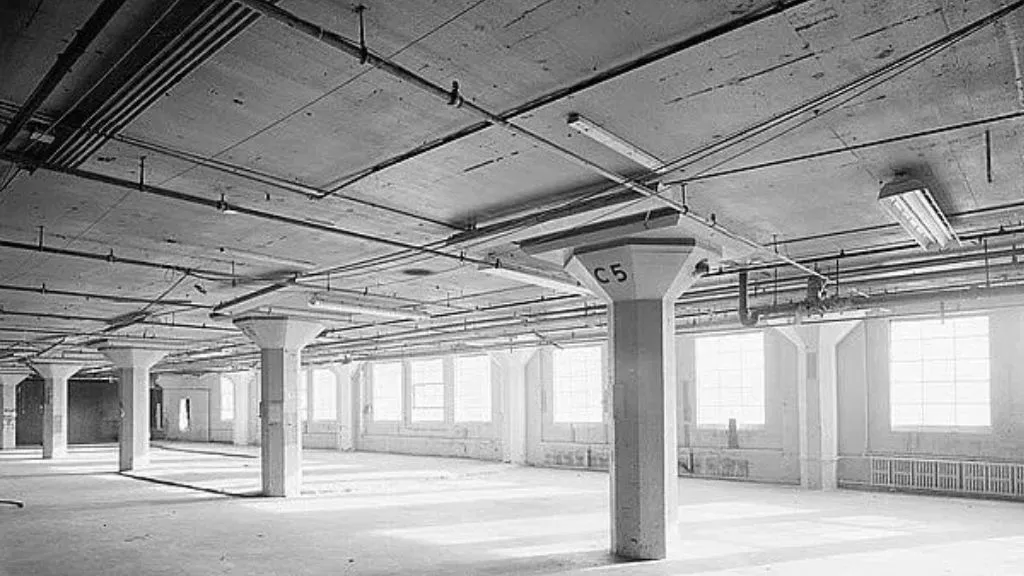

A flat slab is a reinforced concrete slab without any beams or girders. It directly rests on the columns, providing a simple and flexible structural solution. Flat slabs offer advantages such as increased headroom, easy installation of services, and efficient construction. They are commonly used in areas where partitions may be frequently reconfigured or in buildings requiring large open spaces.
4. Waffle Slab
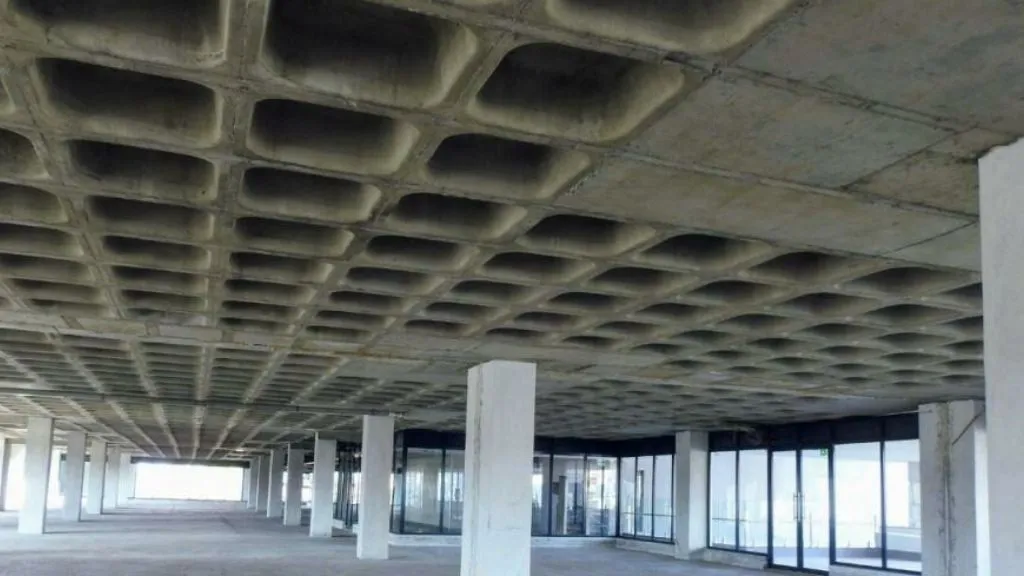

Waffle slabs consist of a reinforced concrete slab with a grid-like pattern of ribs on the underside, forming a series of voids. These voids reduce the weight of the slab while maintaining its structural strength, resulting in a lightweight and economical solution. Waffle slabs offer excellent load-carrying capacity, enhanced stiffness, and improved fire resistance.
5. Post-Tensioned Slab
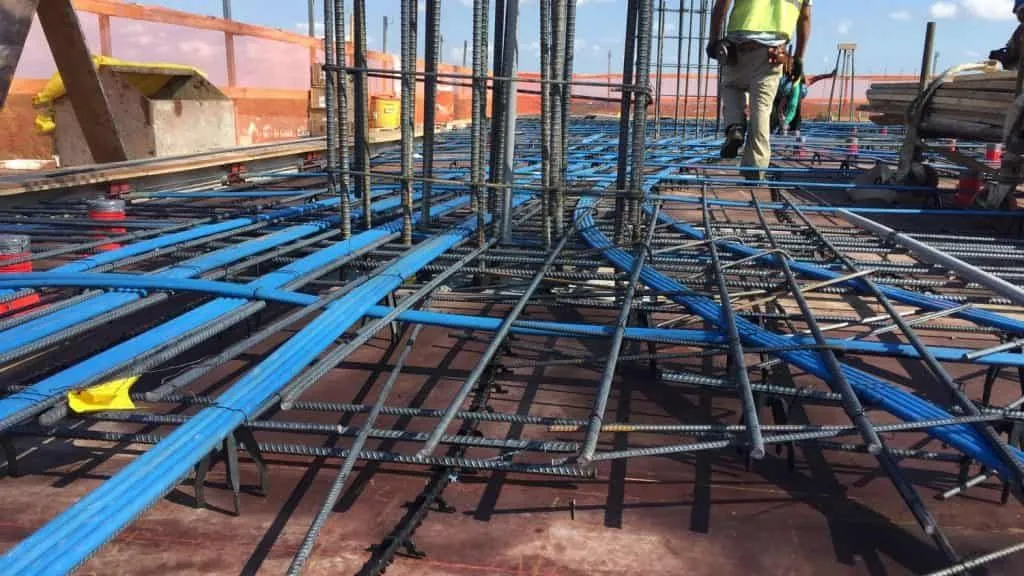

Post-tensioned slabs are reinforced concrete slabs that incorporate high-strength steel tendons tensioned after the concrete has been cast. The tendons are typically placed in a grid pattern and anchored to the edges of the slab. This technique allows for larger spans, reduced cracking, and increased load-carrying capacity, making it suitable for long-span structures such as bridges and parking garages.
6. Precast Slab
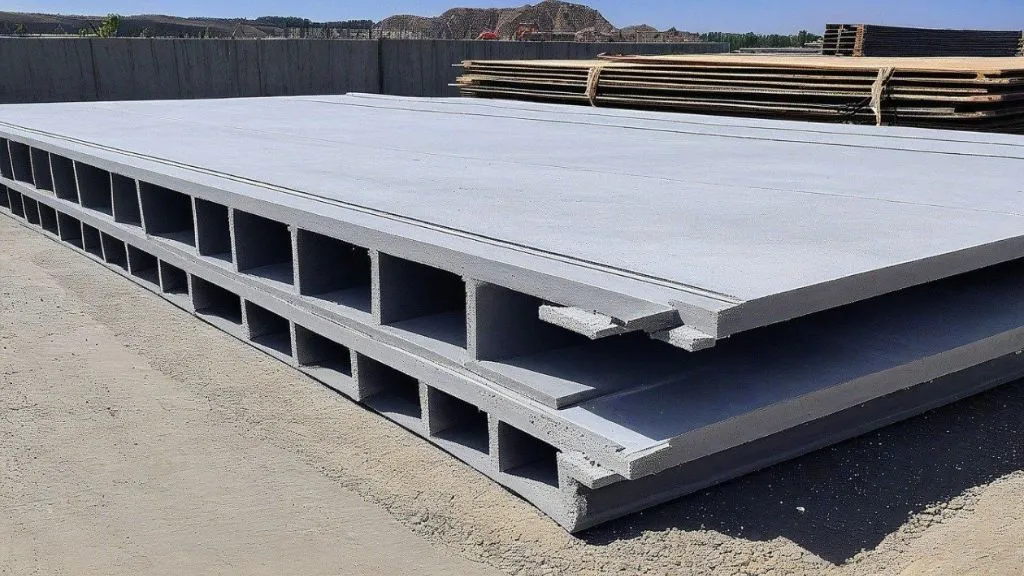

Precast slabs are the types of slabs in construction that are manufactured off-site in a controlled environment and then transported to the construction site for installation. They can be pre-stressed or reinforced and come in various shapes and sizes. Precast slabs offer advantages such as faster construction times, improved quality control, and versatility in design. They are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
7. Ribbed Slab
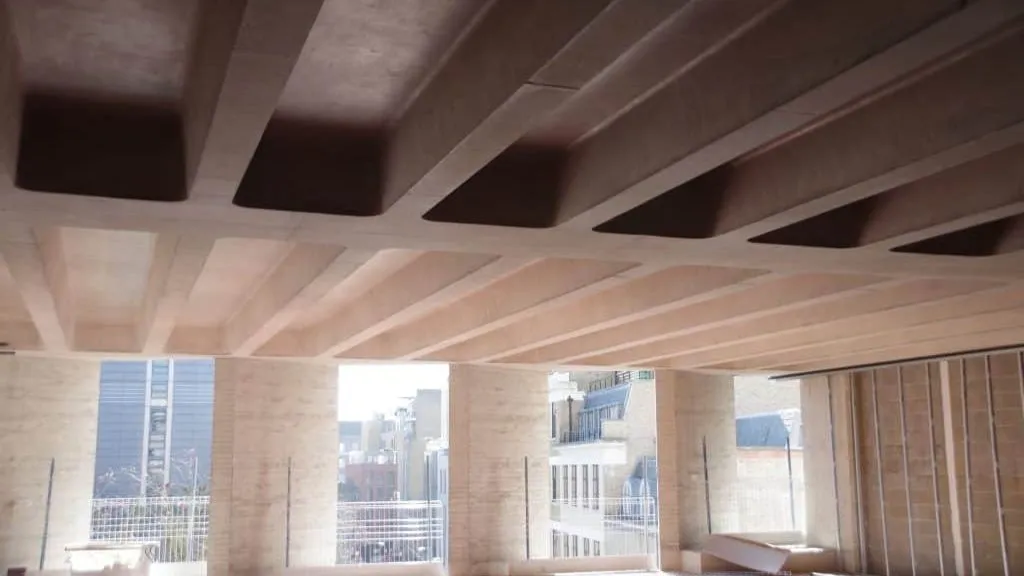

Ribbed slabs consist of a series of parallel reinforced concrete beams or ribs with solid or hollow blocks placed between them. The ribs provide enhanced strength and stiffness to the slab, reducing its weight and improving its load-carrying capacity. Ribbed slabs are commonly used in high-rise buildings, offering advantages such as longer spans, increased flexibility for services installation, and improved thermal and acoustic performance.
8. Beam and Slab
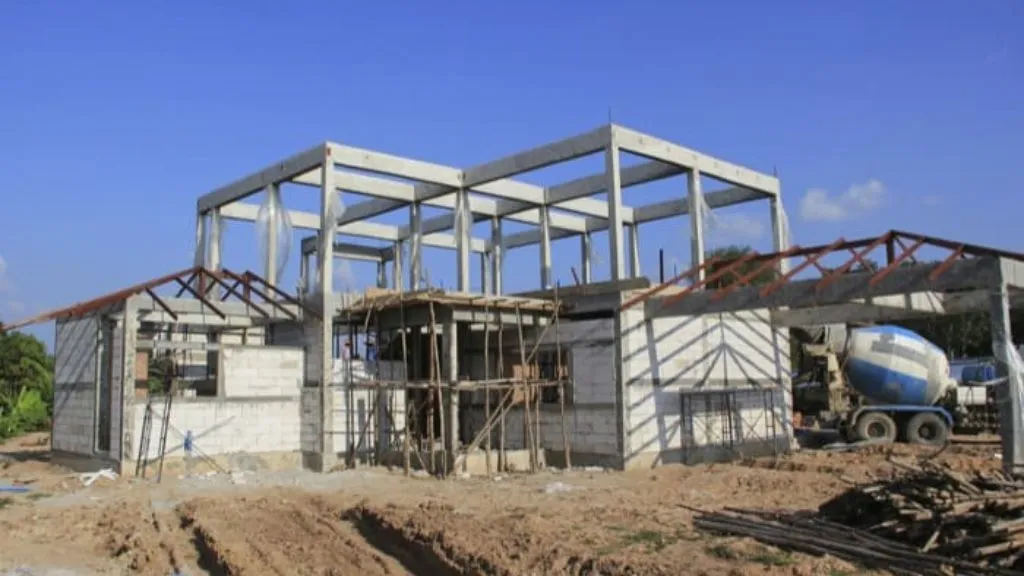

The beam and slab system is a structural arrangement comprising reinforced concrete beams that provide support to the slab. These beams play a critical role in distributing loads and transferring them to the columns or walls. This system is particularly well-suited for structures requiring robust support and accommodating heavy loads or expansive spans, such as bridges and multi-story buildings. By combining the strength of beams with the functionality of slabs, this system ensures structural integrity and enables the construction of resilient and reliable structures.
9. Hollow Core Slab
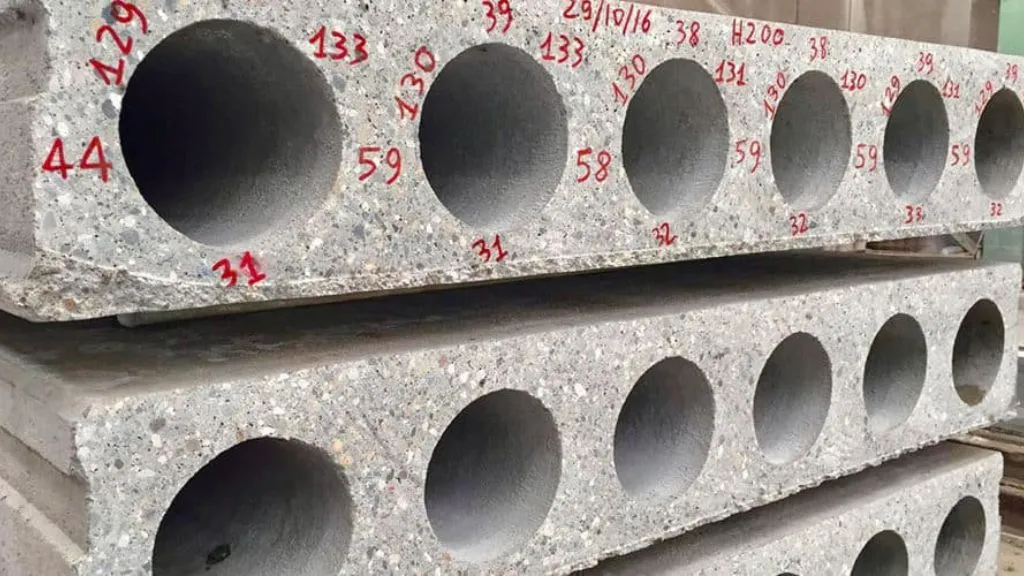

Hollow core slabs are precast concrete elements with hollow cavities running along the length of the slab. These voids reduce the weight of the slab while maintaining its strength. Hollow core slabs are commonly used in floors and roofs of buildings, offering advantages such as efficient use of materials, improved fire resistance, and easy installation of services.
10. Composite Slab
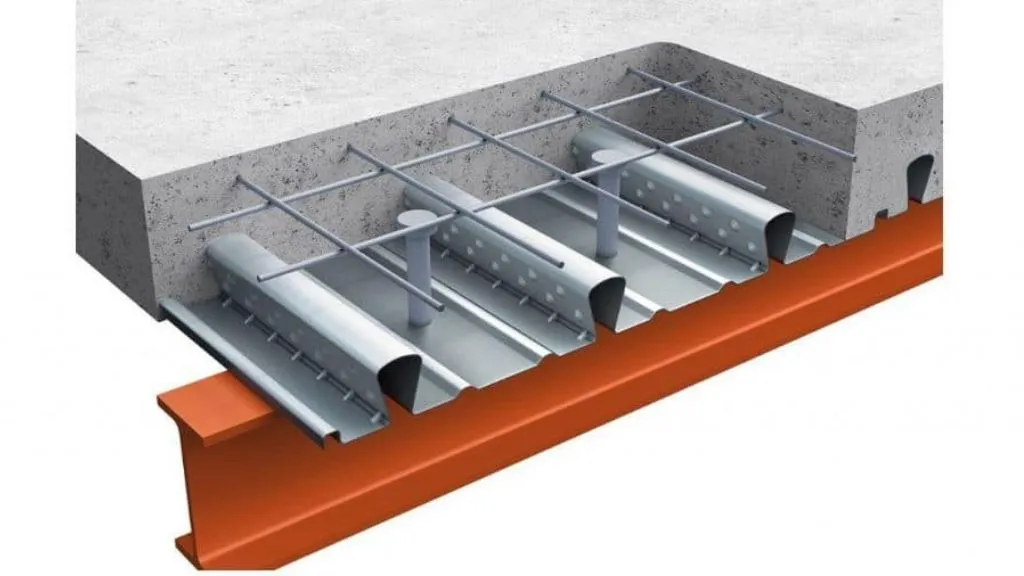

A composite slab is a structural system that combines a reinforced concrete slab with a steel deck, working in unison to withstand loads. During construction, the steel deck acts as formwork and provides tensile strength, while the concrete slab contributes compressive strength. Composite slabs offer several benefits, including an enhanced strength-to-weight ratio, improved fire resistance, and expedited construction processes. By harnessing the complementary properties of steel and concrete, composite slabs provide efficient and durable solutions for a wide range of construction projects.
11. Slab on Grade
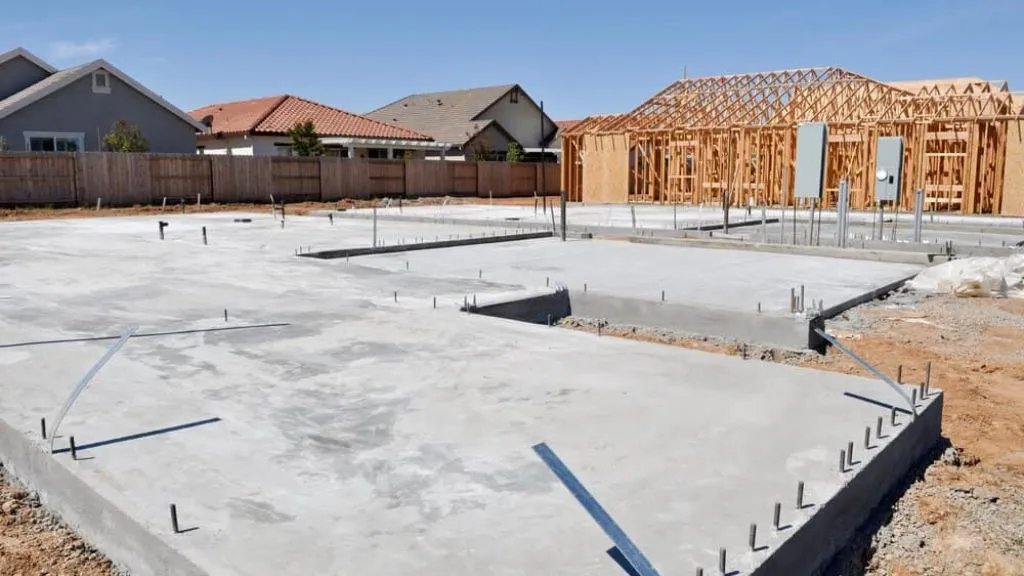

Among the different types of slabs, a slab on grade is directly placed on the prepared ground surface. This type of slab is widely utilized for residential foundations, pavements, and industrial floors. Slabs on grade offer a robust and level surface while efficiently distributing loads uniformly to the underlying ground. They provide stability and durability, making them a popular choice for various construction applications.
12. Suspended Slab
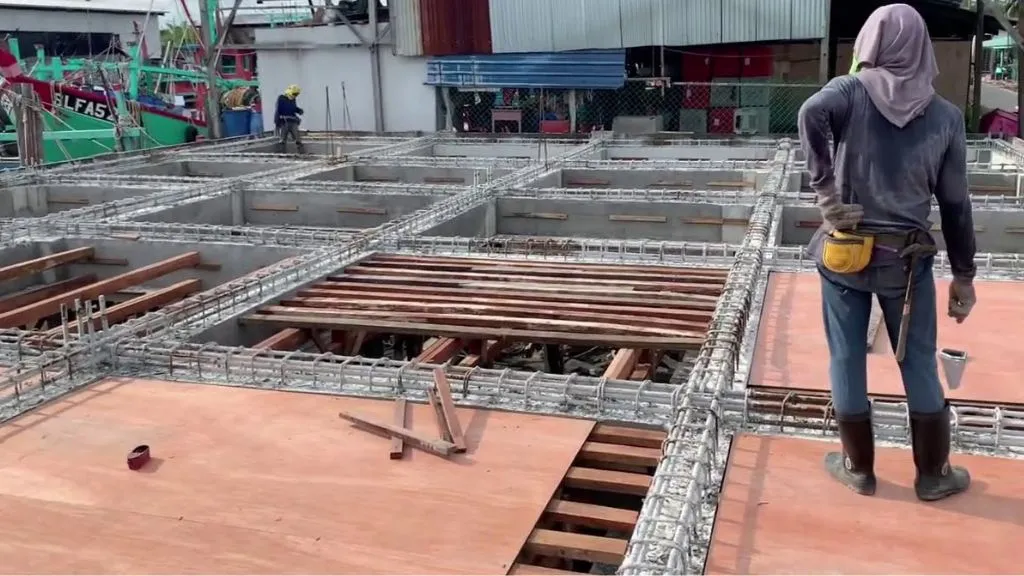

Suspended slabs are the types of slabs that are supported by beams, columns, or walls without direct contact with the ground. It is commonly used in multi-story buildings, where the slabs on upper levels are supported by the structural elements below. Suspended slabs offer flexibility in architectural design, as well as the advantage of creating open spaces and facilitating the installation of services.
13. Bubble Deck Slab
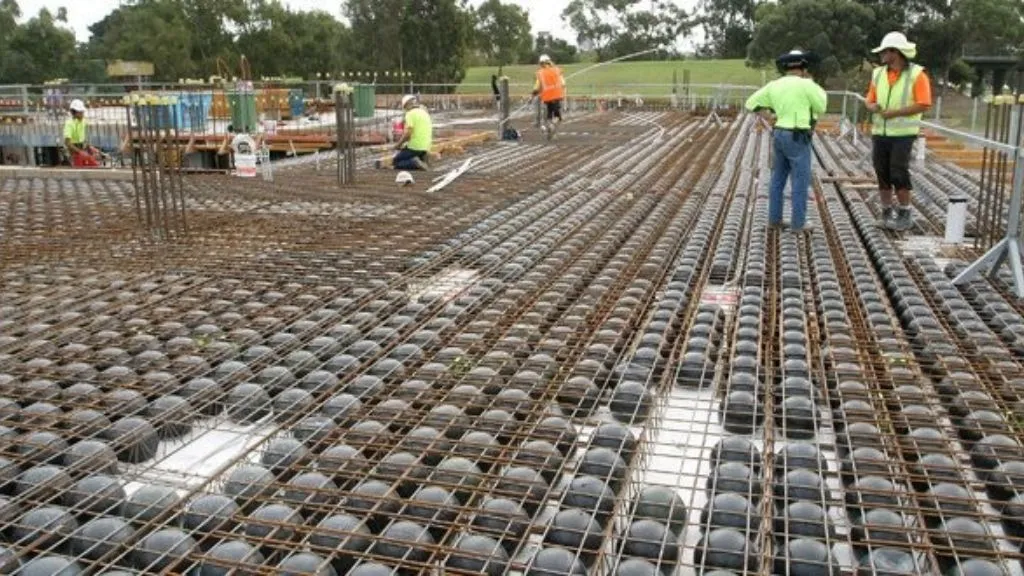

Bubble deck slabs are innovative slabs that incorporate hollow plastic balls or “bubbles” within the slab. These bubbles reduce the weight of the slab while maintaining its strength and load-carrying capacity. Bubble deck slabs offer advantages such as reduced material usage, faster construction times, and improved thermal performance.
14. Slim Floor Slab
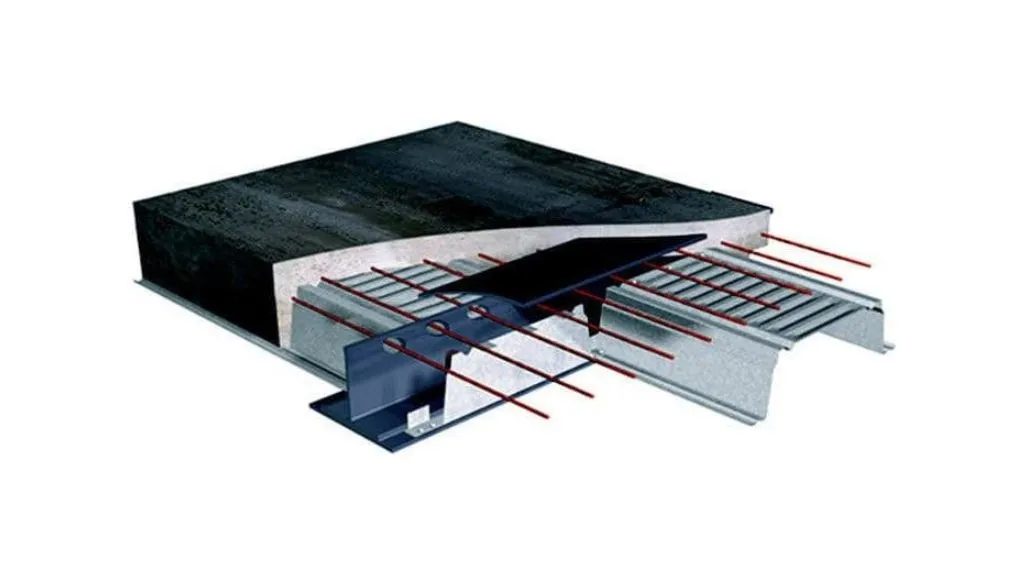

Slim floor slabs are the types of slabs in construction that minimize the overall depth of the floor structure by integrating the beams within the slab thickness. This design allows for a reduced floor-to-floor height and increased flexibility in architectural layouts. Slim floor slabs are commonly used in high-rise buildings, offering efficient use of space and enhanced architectural design possibilities.
15. Hardy Slab
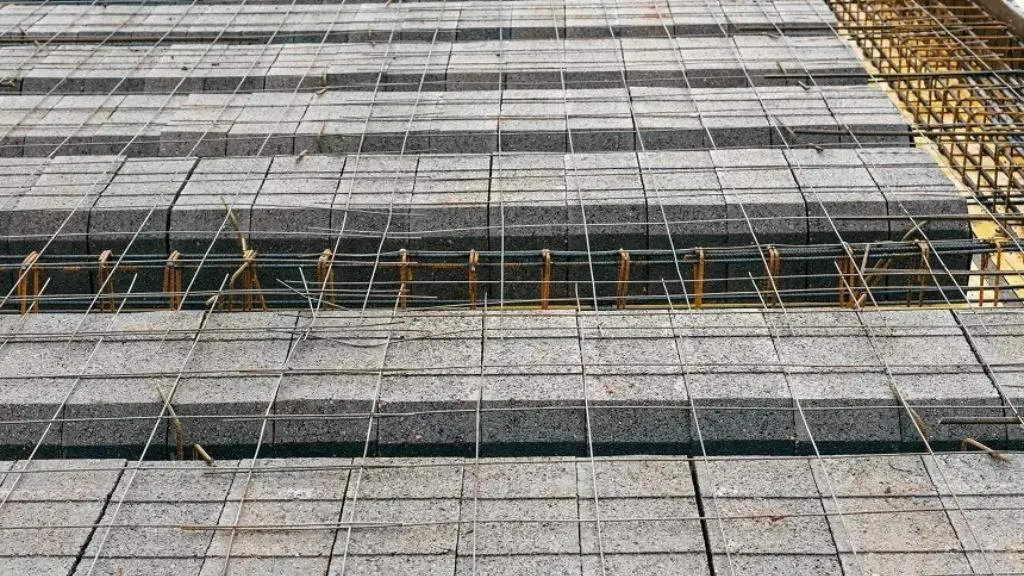

A hardy slab is a type of reinforced concrete slab used for industrial floors subjected to heavy loads, such as warehouses, factories, or loading docks. These slabs are designed to withstand the impact and abrasion caused by industrial activities and provide a durable and stable surface for heavy machinery and equipment.
16. Gypsum Slab

Gypsum slabs are lightweight panels made from a gypsum core sandwiched between layers of paper or fiberglass. They are commonly used for interior partition walls and ceilings in residential and commercial buildings. Gypsum slabs offer advantages such as ease of installation, fire resistance, and sound insulation properties.
17. Lintel Slab
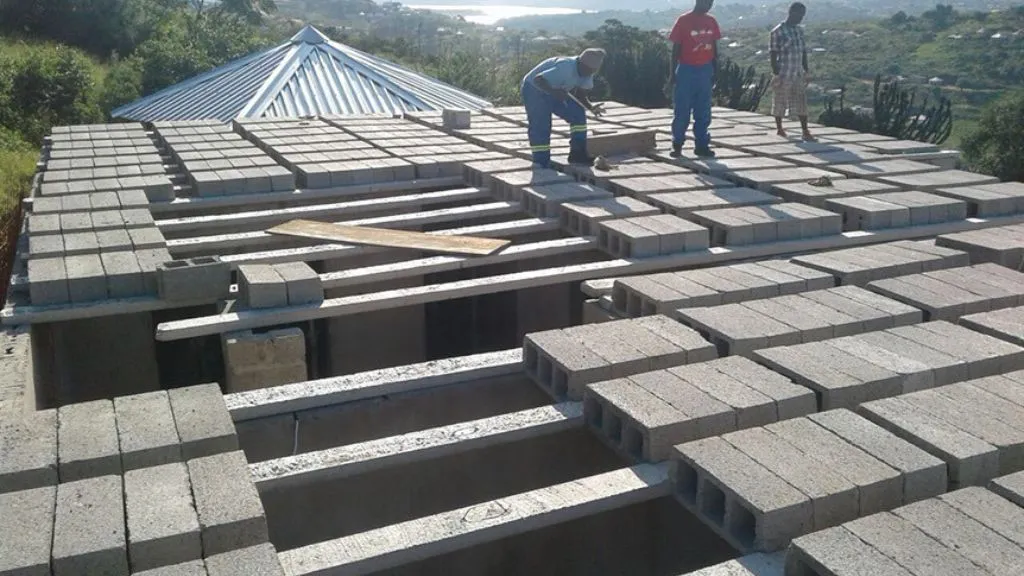

A lintel slab is used to provide support above door or window openings. It spans horizontally between the vertical supports, distributing the loads from the structure above to the surrounding walls. Lintel slabs ensure structural integrity and prevent the openings from sagging or collapsing.
18. Cellular Slab
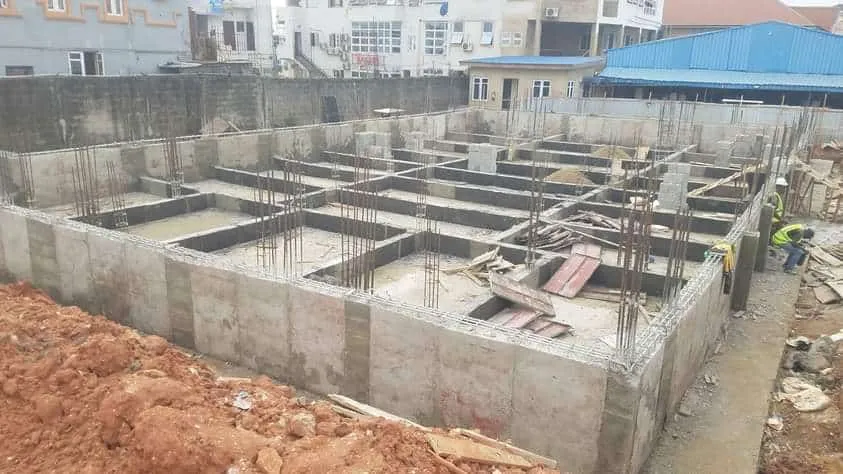

Cellular slabs are composed of interconnected voids or cells within the slab, which are formed using removable forms or void formers. These voids effectively decrease the weight of the slab while preserving its structural integrity, yielding a lightweight and cost-effective solution. Popular in low-rise construction, cellular slabs provide benefits such as enhanced thermal insulation and decreased construction expenses. With their efficient design and advantageous features, cellular slabs offer a practical choice for a variety of building projects.
19. T-Beam Slab
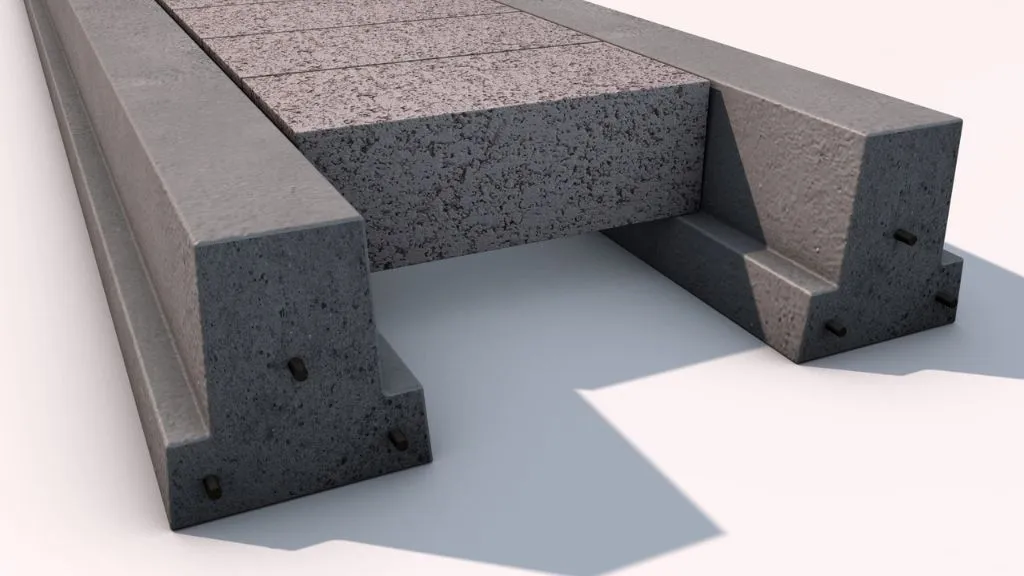
A T-beam slab consists of a reinforced concrete slab with a T-shaped beam at the bottom. The beam provides additional strength and stiffness to the slab, allowing for longer spans and increased load-carrying capacity. T-beam slabs are commonly used in bridges and parking structures.
20. Inverted Beam Slab

An inverted beam slab is a slab with reinforced concrete beams cast on its underside. These beams act as deep ribs and provide additional structural strength and stiffness to the slab. Inverted beam slabs are commonly used in parking structures and industrial buildings, offering advantages such as increased span capabilities and enhanced load distribution.
Conclusion – Different Types of Slabs in Construction
Different types of slabs are vital components in the construction industry, serving as the foundational horizontal surfaces that shape our living and working spaces. They play a crucial role in providing stability, load distribution, and functionality to structures of all kinds. Whether it’s creating solid floors, supporting roofs, or defining ceilings, slabs are integral to the structural integrity and overall design of a building.






